Covalent Compounds Notesheet
advertisement

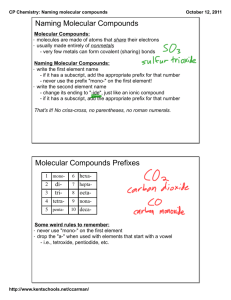
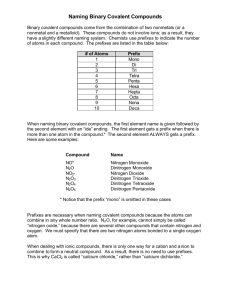
Covalent Compounds (Ch. 7 Sect. 1) Name______________________ Hr____ (Nonmetal-nonmetal) Read "Naming Binary Molecular Compounds", p. 215-217, to answer the following: Unlike ionic compounds, molecular compounds (a.k.a. "covalent" compounds) are composed of individual _____________________ bonded units, or __________________. These substances do not contain ions. The old system of naming molecular (covalent) compounds is based on the use of ___________. For example, the compound CCl4 is named carbon _____________chloride. Likewise, CO is named ___________________________ and CO2 is named ____________________________. These prefix-based names are often the most widely-recognized names. Record the prefixes for the following numbers: 1 6 2 7 3 8 4 9 5 10 Consider the following rules for the prefix system of naming: 1) For the first element listed, the element is given a prefix _________ if it contributes ____________________________________ to a molecule of the compound. 2) The second element is named by combining: a) a _____________ indicating the number of atoms contributed by the element b) the ____________ of the name of the element c) the ending _________ 3) The ______________ at the end of a prefix is usually _________________ when the word following the prefix begins with another vowel. For example, one would write monoxide and pentoxide instead of ____________________ and ______________________. Record names or formulas for the following: P4O10 _______________________________ _____________ dinitrogen pentoxide N2O ________________________________ _____________ nitrogen monoxide NO2 ________________________________ _____________ dinitrogen trioxide On the back of this page, complete Chapter Review Qs #10 and #11 on p. 240.