Naming Covalent Compounds: Chemistry Presentation
advertisement

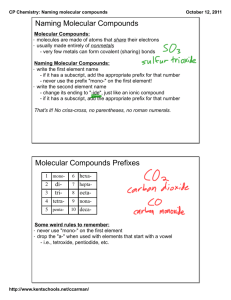
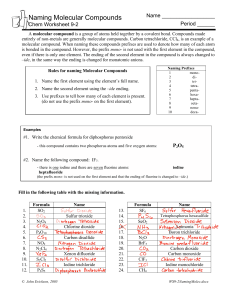
Naming Covalent Compounds • To name a covalent compound, same as ionic naming except you use prefixes to represent how many atoms of each element you have – – – – – – – – – – 1 = mono 2 = di 3 = tri 4 = tetra 5 = penta 6 = hexa 7 = hepta 8 = octa 9 = nona 10 = deca Naming Molecular Compounds 1. write the name of the element that is the least electronegative first. Example: SO2 sulfur 2. Write the name of the second element and change the ending to “ide” Example: SO2 sulfur oxide 3. Add a prefix to the beginning of each element’s name to indicate how many of atoms of each there are (exception: you do not write the word mono in front of the first element if there is only one). Example: SO2 sulfur dioxide • If the vowel combination o-o or a-o appear next to each other in the name, the first of the pair is omitted Example: CO 1. Carbon 2. Carbon oxide 3. Carbon monooxide carbon monoxide Practice Problem 1 Name the following molecular compound: CCl4 Practice Problem 2: Name the following molecular compound: N2O4 Exceptions to the naming rule: • Hydrocarbons/Organic compounds/Alkanes – Compounds made only of carbon and hydrogen and single bonds • • • • • • • • • • CH4 = methane C2H6 = ethane C3H8 = propane C4H10 = butane C5H12 = pentane C6H14 = hexane C7H16 = heptane C8H18 = octane C9H20 = nonane C10H22 = decane • If contains double bond – alkenes – Change ending to –ene – ethane ethene • If contains triple bond – alkynes – change ending to –yne – Propane propyne Exceptions to the naming rule: • Common Names – H2O = water – NH3 = ammonia Writing Molecular Formulas • Name tells you the elements present and the number of each atom to write as subscripts. Example: nitrogen trifluoride Practice Problem 3: Write the molecular formula for tetraphosphorus decoxide. Practice Problem 4: Write the molecular formula for dinitrogen monoxide.