Unit II Learning Targets
advertisement
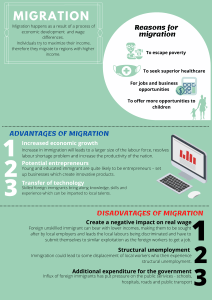
Geography 2A. 2B. 2C. 2D. 2E. 2F. 2G. 2H. 2I. 2J. Name___________________________ Unit 2: Population Study Guide and Learning Targets Test: Pts: I can locate where the world’s population is clustered. (Chapter 2.1) I can differentiate between arithmetic, physiological and agricultural density. (2.2) I can apply indicators of population change among different regions. (2.3) I can construct a population pyramid. (2.4) I can analyze a country’s population based on the demographic transition model. (2.5) I can summarize factors that have led to declining birth rates in developing countries. (2.6) I can identify how geographers predict future population patterns. (2.7) I can define migration, emigration, and immigration. (3.1) I can apply push and pull factors as they influence migration decisions. (3.5-3.7) I can compare and contrast opposing viewpoints on U.S. immigration policy. (3.7-3.9) 2.1 Population Concentrations World Population (number) Population Clusters Sparsely Populated Regions 2.2 Population Density Arithmetic density arable land Physiological density agricultural density Density 2.3 Components of Change Natural increase rate Crude birth rate Crude death rate 2.4 Population Structure Total Fertility Rate Infant mortality Rate Life expectancy dependency ration Population pyramid 2.5 Demographic Transition Model Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Stage 5 2.6 Declining Birth Rates Methods to lower birth rates 2.8 Mathus’s Grim Forecast Theory vs Reality 2.9 Epidemiologic Transition Epidemiologic transition epidemiology Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 2.10 Global Reemergence of Infectious Diseases Reasons for possible Stage 5 (DTM) 3.1 Global Migration Patterns Migration Emigration Immigrant Chain Migration 3.2 Changing Origin of US Immigrants 3 main eras of US Immigration 3.3 Interregional Migration International Migration internal migration Interregional migration- examples in US 3.5 Reasons to Migrate Push Factor Pull Factor Political Factors refugee Economic factors environmental factors 3.7 Gender & Family Gender of migrants education of migrants 3.8 Undocumented US Immigrants Country of Origins unauthorized workers Children labor force Distribution 3.9 Attitudes towards immigrants Quotas