Chapter 4 Notes
advertisement

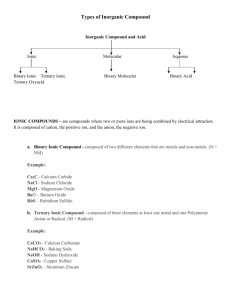
Nomenclature Notes Learning Check Identify the following as covalent(M), ionic(I), or acid(A) bonding: NH4HCO3 ____________ Zn(NO3)2 ____________ CO ________________ KBrO3 ________________ CuI ________________ HF ________________ SF2 ________________ HNO3________________ N2O ________________ Cu2O ________________ CaBr2 ________________ Ba3(PO4)2 ______________ Molecular Compounds Formed by: • 2 or more nonmetals sharing electrons Naming Steps 1. Name first nonmetal with prefix IF subscript > 1 2. Name second nonmetal with prefix ALWAYS & change suffix to –ide Prefixes Mono = 1 Tetra = 4 Hepta = 7 Di = 2 Penta = 5 Octa = 8 Tri = 3 Hexa = 6 Nona = 9 Deca = 10 Formulas • Translate prefixes, prefix = subscript Examples: N2O = Dinitrogen monoxide dihydrogen monoxide = H2O Si8O5 = Octasilicon pentoxide tetrasulfur hexachloride = S4Cl6 NH3 = Nitrogen trihydride carbon monoxide = CO P3I10 = Triphosphorus deciodide carbon dioxide = CO2 Learning Check - Covalent Bonding • Write the names for the following covalent molecules: P4S5 ________________________ SeF6 ________________________ Si2Br6 ________________________ SCl4 ________________________ B2Si ________________________ • Write the formulas for the following covalent molecules: • antimony tribromide ____________________ • hexaboron monosilicide __________________ • hydrogen moniodide _____________________ • iodine pentafluoride _____________________ • dinitrogen trioxide ______________________ • • • • • Ionic Bonding – Naming Compounds Formed by: Metal transferring e- to nonmetal cation: positive ion formed by metal losing eanion: negative ion formed by nonmetal gaining eoppositely charged cation and anion attract to form ionic bond Ions Formed 0 +1 +3 ±4 -3 -2 -1 +2 varies Naming Ionic Compounds Naming Steps 1. Name cation first 2. Give cation roman numeral indicating value of charge I, II, III, IV, V, VI, … EXCEPTIONS: the following metals DO NOT receive a roman numeral Alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, aluminum, silver, zinc, cadmium Reverse criss-cross & raise 3. Name anion with –ide suffix – EXCEPTIONS: polyatomic ion names are not altered Examples: NaCl = sodium chloride KNO3 = potassium nitrate MgBr2 = magnesium bromide CuO = copper (II) oxide Li2SO4 = lithium sulfate Cu2O = copper (I) oxide K3N = potassium nitride SnS2 = tin (IV) sulfide Learning Check - Ionic Bonding • Write the names for the following ionic compounds: • SrS _____________________________ • Cu2S ____________________________ • Be(OH)2 __________________________ • K2CO3 ____________________________ • Mn(NO3)3 _________________________ Formulas 1. Write symbol and charge on cation Roman numeral = charge EXCEPTIONS: the following metals only have one charge possible alkali metals +1, alkaline earth metals +2, aluminum +3, silver +1, zinc+2, cadmium +2 2. Write symbol and charge on anion 3. Select subscript* that makes lowest ratio of charges so, TOTAL POSITIVE CHARGE = TOTAL NEGATIVE CHARGE criss-cross & reduce *formula of polyatomic ion formula in parentheses & subscript outside of parentheses +1 -2 +3 -2 +1 Na O Al S K SO4-2 Examples: Sodium Oxide Aluminum Sulfide Potassium Sulfate Na2O NH4+1 PO4-3 Ammonium Phosphate Al2S3 K2SO4 (NH4)3PO4 +2 -2 Co O cobalt(II) oxide CoO +2 -1 Cu OH copper(II) hydroxide Cu(OH)2 +2 Fe PO4-3 Iron(II) phosphate Fe3(PO4)2 Learning Check - Ionic Bonding Write the formulas for the following ionic compounds: • • • • • potassium fluoride ______________________ magnesium iodide ______________________ ammonium sulfate ______________________ lead (II) nitrite _________________________ lead (IV) sulfite _________________________ Naming Acids Formed by: • H+ bonding with anion Naming Determined by anion • Anion without oxygen: hydro-[root]-ic acid • Anion with oxygen & –ate suffix: [root]-ic acid • Anion with oxygen & –ite suffix: [root]-ous acid Formulas • Translate anion from suffix and prefix • Write H+ with anion Select subscript that makes lowest ratio of charges so, TOTAL POSITIVE CHARGE = TOTAL NEGATIVE CHARGE • criss-cross & reduce HCl = Hydrochloric acid hydroiodic acid = HI HClO3 = Chloric acid hydronitric acid = H3N HClO4 = Perchloric acid nitric acid = HNO3 HClO2 = Chlorous acid nitrous acid = HNO2 HClO = hypochlorous acid sulfuric acid = H2SO4 Learning Check – Acid Bonding • Write the names for the following acids: • H3PO3 ___________________________ HClO2 ___________________________ H2Te ___________________________ HCl ___________________________ HBr ___________________________ • • • • • Write the formulas for the following acids: • hydrocyanic acid ________________________ • hydrofluoric acid ________________________ • phosphoric acid ________________________ • sulfuric acid ________________________ • sulfurous acid ________________________