Midterm Review Game All
advertisement

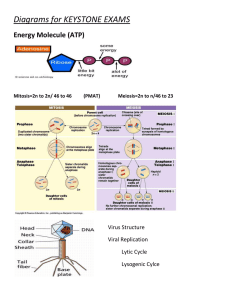
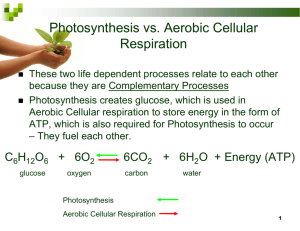
Midterm Review • What invention made the discovery of cells possible, therefore, greatly contributing to the cell theory • Light Microscope • Who invented the compound microscope and looked at pond water? • Anton Leeuwenhoek • Who coined the term “cell”? • Robert Hooke • What was Rudolph Virchow’s contribution to the cell theory? • Cell come from pre-existing cells • Who discovered that animals were made of cells? • Theodor Schwann • Who discovered that plants were made of cells? • Matthias Schlieden • What are the 3 parts to the cell theory? 3pts • 1. All living things are made of cells • 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of living things. • 3. Cells only come from preexisting cells. • The following describes what type of cell: – have no organelles, always unicellular. Ex-bacteria • Prokaryotic • The following describes what type of cell: – Have organelles including a nucleus to store genetic info., much larger than prokaryotes, unicellular & multicellular. Ex- all cells, but bacteria • Eukaryotic • Name 2 organelles that plant cells have that animal cells do not. • Chloroplasts • Cell wall • Name 2 functions of the cell membrane. • • • • Maintain homeostasis Controls what enters and exits the cell Support recognize foreign antigens (germs). • What organic molecules make up cell membranes? • Phospholipids • proteins • What gives plasma membranes strength? • Cholesterol • True or False: • Polar head attracts water and nonpolar tails repel water. • True • True or False: • Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration • False • True or False: • Facilitated diffusion is a form of active transport • False • Endocytosis, exocytosis, and “pump” proteins are all examples of what kind of transport? • active • Cells communicate using this kind of protein. • Receptor • What would a cell do in the following environments: • Hypertonic • Hypotonic • Isotonic • Lysosomes to a body system. • Digestive system • What are cilia and flagella used for? • Movement What does this measure? • Mass • What is the metric unit for length? • meter • An explanation for a broad range of observations, facts, and tested hypotheses is called a________________. • Theory • What is the term for a statement of fact meant to describe, in concise terms, an action? It is generally accepted to be true and universal. • Law • Name 3 characteristics of life. 3pts • • • • Metabolism Homeostasis Growth and reproduction Evolution • Give an example of an abiotic factor and a biotic. 2pts • Abiotic: rock, water, pH • Biotic: deer, humans, grass • What is the climax community in Virginia? • Hardwood forest (hickory and oak) • What is an example of a pioneer species? • Lichen (moss) • What biome do we live in? • Temperate forest • Give an example of the following: pts • Heterotroph • Autotroph • If rain seeps into the soil deeply enough it will become ______________. • Ground water • What geochemical process release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere and oceans? • Volcanoes • What organism drives the nitrogen cycle? • Bacteria • What type of succession would happen after a Volcanoe? • Primary • What type of succession would happen after a fallen tree? • Secondary • What is carrying capacity? • The largest number of individuals of a population that an ecosystem can support. • The symbiotic relationship between a bee and a flower is called what? • Mutualism • What is a symbiotic relationship in which one organism is harmed and the other is unaffected? • Commensalism • What is a catalyst? • And enzyme that speeds up a reaction • How do enzymes speed up reactions? • By lowering the activation energy • 1. The enzyme binds to a reactant in a chemical reaction called the ______________. • 2. The part of the enzyme where the substrate binds is called the ______________. • Substrate, active site • What is the name of the model in the last question? • Lock and key • Name the 4 macromolecules. • Protein, lipid, nucleic acids, carbohydrates • Give an example of a nucleic acid. • DNA, RNA • What is the monomer of lipids • Fatty acids and glycerol • Is water polar or nonpolar • polar • What is it called when water molecules stick to other water molecules? • Cohesion • Why is it important that ice floats on water? • It prevents lakes and ocean from freezing solid. • Both lipids and carbohydrates are important in animal cells because both — • store energy • Write out the entire reaction for photosynthesis. • 6CO2 + 6H2O + light → C6H12O6 + 6O2 • Write out the entire reaction for cellular respiration. • C6H12O6 + 6O2 →6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP • What organelle does photosynthesis take place in? • Chloroplast • What organelle does cellular respiration take place in? • Mitochondria • What are the 2 steps in photosynthesis? • Light independent reactions • Light dependent reactions • What are the 3 steps in Cellular Respiration? • Glycolysis • Krebs cycle • Electron transport chain • What happens in glycolysis? And where does it occur? (2pts) • glucose is broken down to a smaller molecule called pyruvic acid (in cytoplasm) • How many ATP does Cellular Respiration produce? • 34-38 • The passing of electrons along a series of molecules, releasing energy as they go, is known as a(n) -- • Electron transport chain • How many ATP does fermentation produce? • 2