Chapter 8 - Hackittbio
advertisement

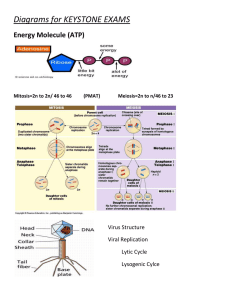
Chapter 8.1-Energry and Life Chemical Energy In Cells - Is stored as ATP - Adenosine triphosphate - Adenine, ribose, 3 phosphate groups - Bonds in ATP can be broken to release energy - Is re-usable - ATP can be re-formed to store energy over and over - Is similar to a rechargeable battery Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) + = + = Phosphate group (P) Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) Autotrophs and Heterotrophs - Autotrophs make their own food - Also called producers - Photosynthesizers - Heterotrophs eat or consume food or nutrients - Also called consumers Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores - Autotrophs form the basis of any chain, and make life on Earth possible Chapter 8.2 p. 232 An overview of photosynthesis Photosynthesis Reaction - Occurs in chloroplasts - In symbols: 6CO2 + 6H2O + light → C6H12O6 + 6O2 - In words: Carbon Dioxide + Water + Light → Sugar + Oxygen Chapter 9.1 p. 251 An overview of cellular respiration Cellular Respiration Reaction - Occurs in mitochondria - In symbols: 6O2 + C6H12O6 + → 6H2O + 6CO2 + ATP - In words: Oxygen + Sugar (Glucose) → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy Chapter 9.1 p. 253 Comparing photosynthesis and cellular respiration Comparing Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration - Removes CO2 from the atmosphere - Releases O2 into the atmosphere - Turns CO2 into food (sugar) - Releases CO2 into the atmosphere - Removes O2 from the atmosphere - Uses O2 to turn sugar into energy