A tissue is defined as a group of similar cells with their extracellular
advertisement

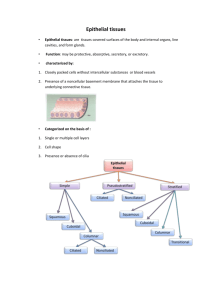
General Histology Epithelium Blood Fertilization: formation of zygote Cleavage: becoming multicellular Gastrulation: fomation of 3 primary tissues – ectoderm, endoderm, mesoderm Tissues of adult organism A tissue is defined as a group of similar cells with their extracellular products, specialized in common direction and set apart for the performance of a common function About 200 types of specialized cells in adult human body are arranged into 4 main tissues: • Epithelium • Blood and connective tissues • Muscular tissues • Nervous tissues Tissue formation is called Histogenesis Tissues are studied in General Histology course Epithelium Epithelium hallmarks • Epithelium covers body surfaces, lines body cavities, and constistutes glands, therefore it is subdivided into lining and glandular • Epithelium creates a selective barrier between the external environment and the underlying connective tissue • The cells predominate, they are closely apposed and adhere to one another by means of special junctions • Their basal surface is attached to an underlying basement membrane • Apical surface may contain nicrovilli and cilia Classification of lining epithelia Location of different types epithelium SIMPLE SQUAMOUS Lining of vascular system Lining of body cavities Bowman`s capsule Lining of lung alveoli SIMPLE CUBOIDAL Small ducts of exocrine glands Surface of ovary Kidney tudules Location of different types epithelium SIMPLE Lining of small intestine COLUMNAR: and colon Stomach and gastric glands Lining of gallbladder PSEUDOSTRATIFIED Lining of trahea and bronchi Lining of ductus deferens Efferent ductules of epididymis Location of different types epithelium STRATIFIED SQAMOUS: Epidermis Lining of oral cavity and esophagus Lining of vagina STRATIFIED CUBOIDAL: Sweat glands, ducts Lager ducts of exocrine glands Anorectal junction Location of different types epithelium STRATIFIED COLUMNAR: Largest ducts of exocrine glands Anorectal junction TRANSITIONAL: Renal calyces Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra Specialized surfaces of epitheliocytes • Apical specializations: - microvilli and cilia • Lateral specializations: - zonulae occludentes - zonulae adherentes - maculae adherentes - gap junctions • Basal specializations: - hemidesmosomes - basal striations Microvilli and terminal web Structure of a cilium Electron micrographs of cilia Lateral specializations of epitheliocytes Classification of glands Multicellular exocrine glands classifiication Modes of secretion: A – holocrine; B – merocrine; C - apocrine