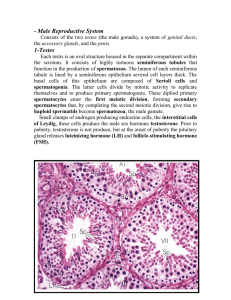
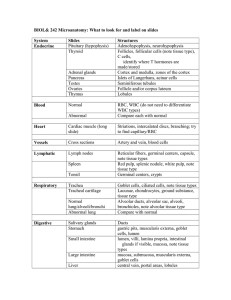
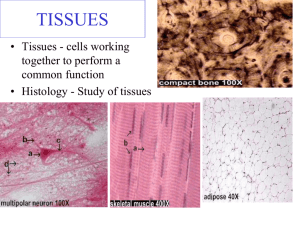
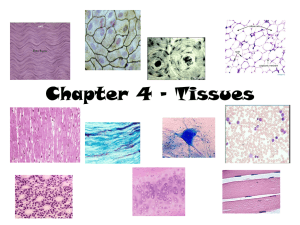
Epithelial tissues
advertisement

Epithelial tissues • Epithelial tissues: are tissues covered surfaces of the body and internal organs, line cavities, and form glands. • Function: may be protective, absorptive, secretory, or excretory. • characterized by: 1. Closely packed cells without intercellular substances or blood vessels 2. Presence of a noncellular basement membrane that attaches the tissue to underlying connective tissue. • Categorized on the basis of : 1. Single or multiple cell layers 2. Cell shape 3. Presence or absence of cilia Type of epithelium Subclassification 1 simple Squamous Lining blood vessels (endothelium), lining body cavities(mesothelium), alveoli of lungs, and loop of Henle of kidney Cuboidal Collecting tubules of kidney, small ducts of exocrine glands, thyroid gland, pancreas, sweet glands, salivary glands, surface of ovary, retetestis Columner Pseudostratified Stratified Squamous Subclassification 2 Site Ciliated Fallopian tubes and small bronchi of lungs Non-ciliated Gall baldder, Collecting ducts of kidney, endocervix, digestive tract from stomach to anus Ciliated Respiratory tract including nose and sinuses Non- ciliated Parts of male urethra and in large ducts of parotid salivary gland NonKeratinizing Lining oral cavity, epiglottis, oesophagus, anus, cervix, vagina, cornea Keratinizing Skin (Epidermis) Cuboidal Large ducts of exocrine glands, ducts of sweet glands, in sperm-forming tubules of testis Columner Conjunctiva, parts of pharynx and eplglottis, and anal canal Transitional Lower urinary tract (renal pelvis, ureters, bladder and urethra)