Unit 8 – Classification and Viruses/Bacteria Independent Practice
advertisement

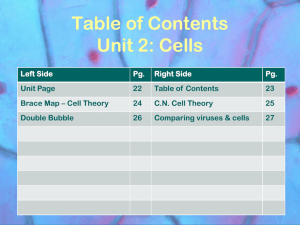
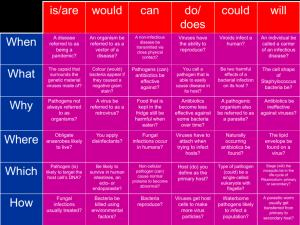
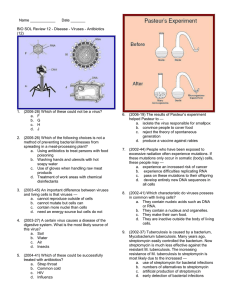
Unit 8 – Classification and Viruses/Bacteria Independent Practice Name: __________________________ 1. What is used to kill bacteria? Antibiotics 2. How does HIV affect a person? Damages immune cells in the process of using the cell to reproduce 3. What must viruses have in order to reproduce? Host cell 4. How does the virus use the host cell? Hijacks or takes over the host cell & uses it to make new viruses 5. What’s the difference between the lytic and lysogenic cycles of viruses? Lytic – quick onset of symptoms Lysogenic – delayed onset of symptoms 6. What would an immunologist want to know about a virus to prevent it from spreading? How to prevent the virus from entering the cell 7. Why can’t antibiotics be used to treat a virus? How are viruses treated? Antibiotics are only used to kill bacteria. Viruses are prevented with vaccines. 8. What role do microorganisms play in natural habitats? Decomposers that recycle nutrients 9. Fill in the Venn diagram to represent the similarities and differences of a cell and viruses. Label each of the following below: Bacteria cell Nonliving Flu, HIV, Herpes Vaccines Need host cell DNA or RNA All bad Genetic material Can cause disease Living Strep throat Antibiotics Good & bad Reproduce on own Binary fission or conjugation Virus 10. Explain why people with AIDS often develop many other infectious diseases? Their immune system is suppressed or weakened due to so many immune cells being destroyed. 11. C A D B B D A C Plant cell Animal cell 12. Why do taxonomists assign each organism a universally accepted name? (Homo sapien) Common classification & naming of organisms Use the cladogram to the right for 13 & 14: 13. What trait separates lampreys from tuna? Jaws 14. All organisms to the right of the tuna would have what characteristics in common? Vertebral column, jaws, four walking legs 15. List the Kingdoms and give 2 distinguishing characteristics for each one. a. Archaebacteria – extremists, prokaryotic, unicellular b. Eubacteria – true bacteria, prokaryotic, unicellular, cell wall with peptidoglycan c. Protista – eukaryotic, mostly unicellular except algae, can be auto or heterotrophic, cell wall of cellulose if present d. Fungi – cell wall of chitin, multicellular except yeast, absorptive heterotroph, decomposers, non-motile e. Plantae – multicellular, eukaryotic, autotroph, non-motile, cell wall of cellulose f. Animalae – multicellular, eukaryotic, heterotroph, NO cell wall, non-motile 16. Which organisms in the chart are more closely related and why? they have more classification levels in common. Label and write the function of the parts of a virus 1. Genetic material (DNA or RNA) – takes over the host cell 2. Capsid – protection 3. Spikes/projections – attachment Common dolphin & killer whale because Dumb Kids Playing Catch On Freeways Get Squashed