Unit 1: Structures and Functions of Living Organisms 8.L.1
advertisement

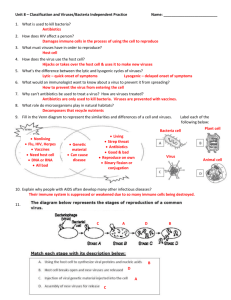
PART ONE: BASIC CHARACTERISTICS OF VIRUSES, BACTERIA, FUNGI, AND PARASITES: AGENTS OF DISEASE MICROBIOLOGY- the study of microorganisms . • A microorganism or microbe is a microscopic organism that comprises either a single cell (unicellular) or cell clusters. • The study of microorganisms is called microbiology, a subject that began with Anton van Leeuwenhoek's discovery of microorganisms in 1675, using a microscope of his own design. • Microorganisms are very diverse; they include bacteria, fungi, archaea, and protists; microscopic plants (green algae); and animals such as plankton and the planarian. Some microbiologists also include viruses, but others consider these as nonliving. Why? All living things (organisms) have 5 characteristics • • • • • Composed of cells Perform chemical processes such as growth and digestion They reproduce Make their own nutrients or ingest them from their habitat Respond to stimuli such as light or touch VIRUSES only do ONE of these! They reproduce. That’s it. • • So what exactly are viruses? Really they are just genetic material bacteriophage (plant virus that attacks bacteria) They ride around in these alien-looking microscopic things that are less than a nanometer. IMPORTANT! They can only replicate within a host cell. They destroy the host cell they are in. Bacteriophage in action • http://www.youtube.com/watch?NR=1&feature=fvwp&v=xXb yJNRwjlg • IMPORTANT! They can only replicate within a host cell. They HARM the host cell they invade. The virus uses the spikes to recognize and attach to the cells they infect. • Works like a “lock and key”. The key fits the lock so the host cells internalize viruses because the host cell "thinks" the virus is something it "wants", such as food, a hormone, etc. Because it only works like a lock and key, viruses have specificity of infection. Certain viruses can only attack certain host cells. Examples of Viruses • ff Foot and Mouth Virus Influenza Virus