Name: Answer Key Microorganism Review What is a controlled
advertisement

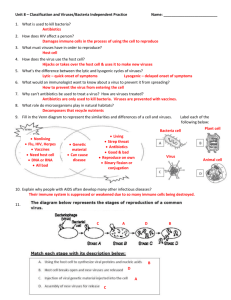
Name: Answer Key Microorganism Review 1. What is a controlled experiment? Give an example of a controlled experiment. A controlled experiment is when all factors of the experiment is the same except for one. An example of a controlled experiment was the bread-mold experiment we completed as a class. 2. What is the difference between a multicellular organism and a unicellular organism? A multicellular organism is made up of many cells. Unicellular organisms are made up of one cell. 3. What is the difference between a heterotroph and an autotroph? Autotrophs can make their own food. Heterotrophs cannot make their own food. 4. What is the difference between a prokaryote and a eukaryote? A eukaryote contains a nucleus. Prokaryote does not have a nucleus. 5. Why are antibiotics ineffective against viral infections? Antibiotics can only kill bacteria. Viruses cause viral infections. 6. What is a virus? A virus is a tiny non-living particle that enters and then reproduces inside a living cell. 7. Name an organism that is safe from a virus. There is no organism that is safe from a virus. 8. What is smaller a virus or a cell? How do you know? A virus is smaller. A virus enters inside the cell. 9. How does protein help a virus invade a host cell? The proteins act like the key that opens the lock of the cell. Once inside the cell, the virus takes over the cell and starts reproducing more viruses. 10. How do active viruses and hidden viruses differ? Active viruses enter into the cell and immediately go into action. The hidden viruses will enter the cell and wait and “hide” for a while and then start reproducing more viruses. 11. What is the purpose of the flagellum? The purpose of the flagellum is to help the bacteria/organism to move. 12. What three shapes do bacteria come in? Spiral-shaped, rod-like shaped, spherical 13. What are spores? Spores are the reproduction cells of a fungi and fungus-like protists. 14. What are the three groups of protists? Animal-like protists, Plant-like protists, Fungus-like Protist 15. What are some characteristics of animal-like protists? Heterotroph, also known as Protozoan, move place to place to obtain food, use flagellum and cilia to move 16. What are some characteristics of protists? Autotroph and heterotroph, most unicellular but some are multicellular, some can move and some cannot move. All live in moist surroundings. 17. What are some characteristics of plant-like protists? Autotrophs, produce much of our oxygen, some unicellular and some multicellular. Types – Diatoms, Dinoflagellates, Euglenoids, Red Algae, Green Algae and Brown Algae. 18. What are some characteristics of fungus-like protists? Heterotrophs, cell walls, and use spores to reproduce. Types – Slime Molds, Water Molds, and Downy Mildew 19. What are some characteristics of fungi? Eukaryotes, heterotrophs that obtain food by absorbing food through Hyphae, use spores to reproduce, cause diseases, provides food, fights diseases 20. What is the best treatment for a bacterial infection? Viral infection? The best treatment for a bacterial infection is to use an antibiotic. The best treatment for a viral infection is to get plenty of rest, eating healthy meals, and drinking fluids .