File
advertisement

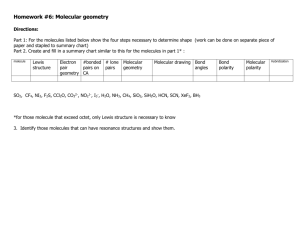
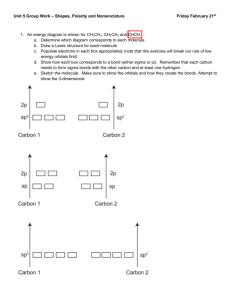
MOLECULAR STRUCTURE GEOMETRIES HYBRIDIZATION POLARITY OF MOLECULES SIGMA AND PI BONDS Chapters 10.2-10.3 & 11.1-11.3 Goals & Objectives See the following Learning Objectives on pages 392 & 419. Understand these Concepts: 10.5-8 & 11.1-10. Master these Skills: 10.4-5 & 11.1-4. MOLECULAR STRUCTURE Draw the Lewis Electron Dot Structure Predict the electronic geometry Predict the hybridization on the central atom Predict the molecular geometry Predict the polarity of the molecule Predict the number of sigma bonds Predict the number of pi bonds Electronic Geometry VSEPR Theory Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory -regions of high electron density about the central atom are as far apart as possible to minimize repulsions electronic geometries are determined by the number of regions of electron density about the central atom Electronic Geometry Regions of Electron Density Geometry 2 linear 3 trigonal planar 4 tetrahedral 5 trigonal bipyramidal 6 octahedral VALENCE BOND THEORY explains structures of molecules in terms of the overlap of atomic orbitals to produce bonds between atoms accounts for electronic geometries by a mathematical combination of atomic orbitals to produce hybrid orbitals that will fit the proposed electronic geometries Hybrid Orbitals Electronic Geometry Hybridization linear sp trigonal planar sp2 tetrahedral sp3 trigonal bipyramidal dsp3 octahedral d2sp3 sp Hybrid Orbitals Figure 11.2 The sp hybrid orbitals in gaseous BeCl2. atomic orbitals hybrid orbitals orbital box diagrams Figure 11.2 The sp hybrid orbitals in gaseous BeCl2(continued). orbital box diagrams with orbital contours sp2 Hybrid Orbitals Figure 11.3 The sp2 hybrid orbitals in BF3. sp3 Hybrid Orbitals Figure 11.4 The sp3 hybrid orbitals in CH4. Figure 11.6 The sp3d hybrid orbitals in PCl5. Figure 11.7 The sp3d2 hybrid orbitals in SF6. Molecular Geometry Electronic Molecular Geometries Geometries linear linear trigonal planar trigonal planar angular tetrahedral tetrahedral angular trigonal pyramidal Figure 10.7 The four molecular shapes of the trigonal bipyramidal electron-group arrangement. PF5 SF4 AsF5 XeO2F2 SOF4 IF4+ IO2F2- ClF3 XeF2 BrF3 I3 - IF2- Figure 10.8 The three molecular shapes of the octahedral electrongroup arrangement. SF6 IOF5 BrF5 TeF5 - XeOF4 XeF4 ICl4- Molecular Geometry Figure 10.9 A summary of common molecular shapes with two to six electron groups. Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry POLARITY OF MOLECULES the polarity of a molecule is the vector sum of the bond polarities of the molecule the bond polarities will either cancel or not SAMPLE PROBLEM 10.9 PROBLEM: Predicting the Polarity of Molecules From electronegativity (EN) values (button) and their periodic trends, predict whether each of the following molecules is polar and show the direction of bond dipoles and the overall molecular dipole when applicable: (a) Ammonia, NH3 (b) Boron trifluoride, BF3 (c) Carbonyl sulfide, COS (atom sequence SCO) PLAN: Draw the shape, find the EN values and combine the concepts to determine the polarity. SOLUTION: (a) NH3 The dipoles reinforce each other, so the overall molecule is definitely polar. ENN = 3.0 H ENH = 2.1 N H H H N H H bond dipoles H N H H molecular dipole SAMPLE PROBLEM 10.10 Predicting the Polarity of Molecules continued (b) BF3 has 24 valence e- and all electrons around the B will be involved in bonds. The shape is AX3, trigonal planar. F B F F 1200 F (EN 4.0) is more electronegative than B (EN 2.0) and all of the dipoles will be directed from B to F. Because all are at the same angle and of the same magnitude, the molecule is nonpolar. (c) COS is linear. C and S have the same EN (2.0) but the C=O bond is quite polar(DEN) so the molecule is polar overall. S C O TYPES OF BONDS SIGMA bonds head-on overlap of atomic orbitals all single bonds are sigma bonds PI bonds parallel overlap the extra bonds TYPES OF BONDS single bonds--sigma bonds double bonds--one sigma and one pi bond triple bonds-- one sigma and two pi bonds CH4 Electronic geometry ____________ Hybridization on the central atom _______ Molecular geometry_____________ Polarity _________________ Number of sigma bonds ________ Number of pi bonds __________ CH4 C2H4 Electronic geometry _________________ Hybridization on the central atom _______ Molecular geometry _________________ Polarity _________________ Number of sigma bonds ________ Number of pi bonds __________ C2H4 C2H2 Electronic geometry _________________ Hybridization on the central atom _______ Molecular geometry _________________ Polarity _________________ Number of sigma bonds ________ Number of pi bonds __________ C2H2 CO32 Electronic geometry _________________ Hybridization on the central atom _______ Ionic geometry _________________ Polarity _________________ Number of sigma bonds ________ Number of pi bonds __________ CO32- BeI2 Electronic geometry _________________ Hybridization on the central atom _______ Molecular geometry _________________ Polarity _________________ Number of sigma bonds ________ Number of pi bonds __________ BCl3 Electronic geometry _________________ Hybridization on the central atom _______ Molecular geometry _________________ Polarity _________________ Number of sigma bonds ________ Number of pi bonds __________ NH3 Electronic geometry _________________ Hybridization on the central atom _______ Molecular geometry _________________ Polarity _________________ Number of sigma bonds ________ Number of pi bonds __________ H2O Electronic geometry _________________ Hybridization on the central atom _______ Molecular geometry _________________ Polarity _________________ Number of sigma bonds ________ Number of pi bonds __________ SCN Electronic geometry _________________ Hybridization on the central atom _______ Ionic geometry _________________ Polarity _________________ Number of sigma bonds ________ Number of pi bonds __________ PCl5 Electronic geometry _________________ Hybridization on the central atom _______ Molecular geometry _________________ Polarity _________________ Number of sigma bonds ________ Number of pi bonds __________ SF6 Electronic geometry _________________ Hybridization on the central atom _______ Molecular geometry _________________ Polarity _________________ Number of sigma bonds ________ Number of pi bonds __________