Guided Review for Chapter 1
advertisement

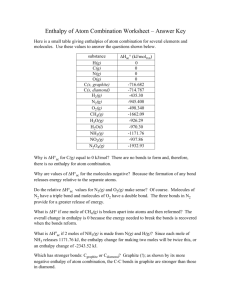
Guided Review for Chapter 1 Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry Chapter 1 covers material you should have covered in previous courses. It will not explicitly be covered in the lecture, but I will test on this material. There is a lot of vocabulary. Please see me in office hour or email me if you have trouble with this material. Terms to know Eukaryote metabolites Prokaryote genome Plasma membrane endoplasmic reticulum (smooth and rough) Cytoplasm Golgi complex Cytosol nucleolus Ribosome cell wall Nucleus glyoxysome Nucleoid vacuole cell envelope plasmodesma cytoskeleton thylakoids mitochondria starch granules organelle membrane nuclear envelope chloroplast peroxisome plasmid lysosome metabolome in vitro in vivo endocytosis stereoisomers exocytosis stereospecific reactions configuration enantiomers conformation diastereomers geometric isomers chiral centers racemic mixture meso compound enthalpy entropy free energy content(Gibbs' free energy) exergonic endergonic exothermic endothermic oxidation oxidizing agent reduction reducing agent dynamic steady state equilibrium pathway metabolism catabolism anabolism catalyst activation energy enzyme transition state native conformation mutation gene photosynthesis electronegativity polar bonds and molecules covalent bonds hydrogen bonding London forces Nucleophile Free radical Polymer non-polar bonds and molecules ionic bonds dipole attractions van der Waals' forces electrophile ion monomer Other Things to Review at this point 1. Organic functional groups: carbonyl, hydroxyl, carboxyl, ester, ether, amides, amino, sulfhydryl, disulfide, thioester, phosphoryl, phosphoanhydride, phosphoester, anhydride, and phenyl, methyl, ethyl groups These are all on figure 1-15 except the phosphoester group. 2. Bonding: valences and covalences of C, N, O, H and S in particular freedom of rotation about bonds (or not) concept of steric hindrance geometry, especially of carbon, with single, double or triple bonds present (linear, bent, pyramidal, tetrahedral) 3. Equation review Expression for the free energy change. (pg. 23) How to write equations for equilibrium constants. (pg. 26) Relationship between standard free energy and the equilibrium constant.(pg. 26) Relationship between free energy and standard free energy (eq. 1-1) Also, recall diagrams that show the course of a reaction (see page 27, figure 1-27). 4. Problems Make sure that as a minimum you review the following problems from chapter 1. 6, 7, 8, 12 Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What distinguishes prokaryotes from eukaryotes. What is the main energy producing organelle in animal cells? Plant cells? What cell structure is the site of protein synthesis? What is the main structural component of membrane structures? What is the genetic material of most organisms and where in the cell is this found? What are the 4 major types of biochemicals? 7. What is different about a catalyzed reaction and an un-catalyzed reaction? 8. What geometry is around the carbon atom in CO2, CH4, CH2O (formaldehyde)? 9. What is the geometry about the oxygen in water? about the nitrogen in ammonia? 10. Which elements are most prevalent in living organisms? 11. What is the difference between configurations and conformations? 12. What criteria for the free energy, enthalpy or entropy make a reaction spontaneous?