Chapter 5 notes
advertisement

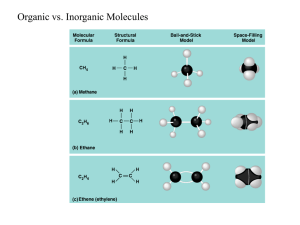
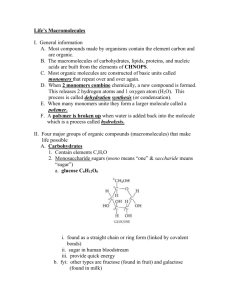
Macromolecules Building Blocks of Life Macromolecules • Smaller organic molecules join together to form larger molecules – macromolecules • 4 major classes of macromolecules: – carbohydrates – lipids – proteins – nucleic acids Monomer + Monomer = Polymer • Carbs, Proteins, Nucleic Acids are made of chainlike repeating units • Chains of single units (monomers) make polymers Polymers • Long molecules built by linking repeating building blocks in a chain – monomers • building blocks • repeated small units – covalent bonds • Why is Carbon so good at this?? How to build a polymer • Dehydration Synthesis: • joins monomers by “taking” H2O out • one monomer donates OH– • other monomer donates H+ • together these form H2O H2O – requires energy & enzymes HO H HO H enzyme Dehydration synthesis HO H How to break down a polymer • Hydrolysis: • use H2O to breakdown polymers • reverse of dehydration synthesis • cleave off one monomer at a time • H2O is split into H+ and OH– – H+ & OH– attach to ends – requires enzymes – releases energy HO H2O enzyme H Hydrolysis HO H HO H 1. Carbohydrates (C,H) • Are sugars and polymers of sugars – Monosaccharides: one sugar – Disaccharides: two sugars – Poly saccharides: more than two sugars • Store short term energy Monosaccharides • Simple sugars that provide short term energy • Ex: glucose Disaccharides • Monosaccharide + Monosaccharide • Formed via dehydration synthesis • Ex: sucose Disaccharide Polysaccharides • Complex starches that store short term energy • Glycogen: hydrolyzed in the liver when sugar supplies are low Structural Polysaccharides • Cellulose: cell walls • Chitin: exoskeletons 2. Lipids (C, H, O, sometimes P) • The smallest of the macromolecules • Not a true polymer (different monomers) – Glycerol head – Fatty acid tail • Storage of long-term energy Fats Steroids Phospholipids • Cell membranes phosphorus 3. Proteins (C, H, O, N, sometimes S) • 3 Dimensional polymers – Monomers: amino acids – Polymer of amino acids is called a polypeptide – Held together by covalent peptide bond – Protein is one or more polypeptides Many Functions • Speed up reactions • Structure • Storage • Transport • Communication • Movement • Defense Amino Acids • 20 amino acids build thousands of proteins • Each one has an amino group, carboxyl group, H, and R-group 4 Levels of Protein Structure • Primary: amino acid chain held by peptide bonds • Secondary: hydrogen bonds between H & carboxyl α-helix or β-pleated sheet 4 Levels of Protein Structure, cont. • Tertiary: Rgroups interact further folding the protein • Quaternary: aggregation of polypeptides Just how important is primary structure? 4. Nucleic Acid (C, H, O, N, P) • Storage of heritable information – DNA and RNA • Monomers: nucleotides – Sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) – Phosphate group – Nitrogen base (A, G, C, T, U) DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid • Genetic material inherited from parents to offspring • Self-replicating • Does not code directly for protein (needs RNA assistance) RNA: ribonucleic acid • Used by the cell to decode DNA’s instructions for protein • DNA RNA Protein • Central Dogma of Genetics