Biology and Biochemistry Study Guide List
advertisement

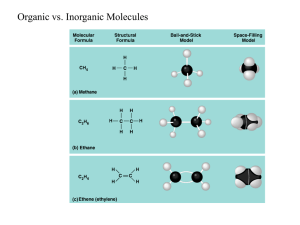
Advanced Biology Study Guide Biology and Biochemistry For your test over biology and biochemistry, you will need to know the following terms and concepts: Biology o Definition o Inorganic vs organic molecules o Hierarchy of living organisms (atomsorganism) Types of tissues o Six components that all living organisms have in common Cell structure Unicellular Multicellular Cell differentiation Metabolism Autotrophs Heterotrophs Evolution Definition Natural selection Reproduction Asexual (definition and examples) Sexual (definition and examples) Homeostasis Definition Examples Response to stimuli o Miller-Urey experiment What happened Importance Atoms o Parts Names Locations in the atom Charge Versions Isotopes Ions o Fission vs fusion Phases of matter o Names of the phases o Volume and shape of each phase o Names of phase changes o Importance of energy in regards to phase changes Kinetic Theory o Postulates Elements, Compounds, Molecules, Mixtures o Definitions of each Homogeneous vs heterogeneous mixtures o Importance of each pH and Water o Solute o Solvent o Concentration o pH Definition pH scale (know where acids, bases, and neutral solutions are) o Acids and bases Relationship with hydrogen ions (released or accepted) Examples Definition of indicators o Buffers Definition Uses/importance Examples in the body o Water Polar vs nonpolar Importance of water in body Cohesion vs adhesion Covalent bonds o Definition o Polar covalent Types (definitions and importance for each type) o Nonpolar covalent (definition) Ionic bonds o Definition o Uses/importance Macromolecules o Monomers vs polymers definition o Carbohydrates Monomer Polymers (examples and importance of each) Importance Condensation vs hydrolysis o Lipids Monomers Polymers (examples and importance of each) Phospholipids (shapes) Importance Saturated vs unsaturated fats Definitions Importance o Proteins Monomers 5 components of this monomer Importance of DNA/RNA to this monomer Polymers (examples and importance of each) Structure (primaryquaternary) o Nucleic Acids Monomers Three parts What determines sequence of bases Polymers (examples and importance of each)