CHAPTER 3 Study Outline Macromolecules CARBON
advertisement

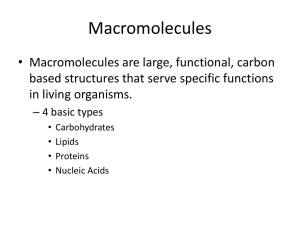
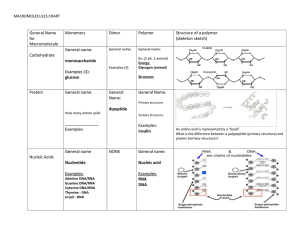
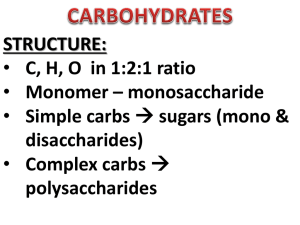
CHAPTER 3 Study Outline Macromolecules CARBON COMPOUNDS Organic vs. inorganic compounds The importance of carbon and carbon bonding in biological molecules How many bonds can carbon form and what types of bonds can carbon form? What are the four major types of macromolecules? What are functional groups? Be able to identify the amino group. Define monomers, Dimers, Polymers How are monomers linked to form polymers? (What is the process?) How are polymers broken down into simpler molecules? (What is the process?) Describe what happens during Condensation Reaction (dehydration synthesis). Describe what happens during Hydrolysis. Describe the role of ATP in the body. Describe how ATP undergoes hydrolysis to provide energy. Identify reactants/products. Identify the components of ATP MACROMOLECULES Carbohydrates – what elements make them up, % in the body o Their role in the body o Their building blocks and the different types o What is an isomer? Examples? o What is a disaccharide? Example? o What is a polysaccharide? Examples? What are the roles of Starch Glycogen Cellulose o What are the main differences between simple sugars and complex carbs? o What are some examples of food that have simple sugars? Complex carbs? Lipids – what elements make them up, % in the body o Their role in the body o Their building blocks and different types o Fatty Acids – carboxyl group Different properties of polar and nonpolar ends Hydrophilic – what does this mean and how does it affect the body? Hydrophobic- what does this mean and how does it affect the body? Saturated fatty acids vs. unsaturated fatty acids o Triglycerides – what are they? Where are they found? Saturated triglycerides (neutral fats) vs. unsaturated Plants vs. Animal fat Building blocks of o Phospholipids Components of Where are they found in the body? What role do they play in the body? o Waxes – what are they? Examples of (where are they found and what do they do?) o Steroids – what are they? Describe structure of Examples of Proteins – what elements make them up, % in the body o Building blocks of o Parts of an amino acid – and their importance Center Carbon Carboxyl group Amino group R group Single H o Dipeptides and polypeptides Peptide bond o Roles of Proteins in the body – provide an example for each Regulatory Contractile Structural Immunological Transport Catalytic (enzymes) Induced-fit model Substrate Active site Activation energy The effect of temperature on enzyme activity TESTING FOR MACROMOCULES Know the tests for Simple Sugars, Starch, Protein, Lipids Know what a positive test result should look like