Principles of Finance – Fall 2012
(FIN 3403)
Instructor: Nina Schmidt, Ph.D.
OUTLINE:
Welcome & Introduction
Syllabus, Blackboard and Connect
Chapter 1
0
1
Chapter 1
Introduction to Corporate Finance
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Chapter Outline
•
•
•
•
•
Financial Management
The Agency Problem
Forms of Business Organization
Financial Markets
Class Overview
3
Financial Management
• Def of Finance:
the study of money
• The goal of the financial manager:
maximize market share or profits?
best: “optimize shareholder value”
4
Financial Management
• The Three Main Decisions (Functions)
of the financial manager:
1. Capital budgeting or investment decisions
2. Capital structure or financing decisions
3. Working capital management or day to
day cash management decisions
(note: we will focus on the corporate world)
5
Sample Organizational Chart
6
The Agency Problem
• An agency relationship is also called
a fiduciary relationship. In an agency
relationship the
represents the
.
• An agency problem exists when a
exists between the agent and
the principal.
• The solution for the agency problem:
tie management compensation to stock price
performance
• Corporate Scandals and Sarbanes Oxley Act
7
of 2002.
Forms of Business
Organization
Sole
Proprietorship
Characteristics:
Partnership
(General or
Limited)
Corporation
Life of Business
Ability to Raise
Cash
Taxation
Liability
Transfer of
Ownership
8
Forms of Business
Organization
• Two forms of business organization
that take advantage of the benefits of
a corporation but avoid double
taxation: S-Corp and LLC.
• Legal information can be found on
legal websites, such as:
www.nolo.com
www.legalzoom.com
9
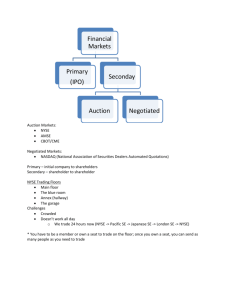
Financial Markets:
Cash Flows between the Firm and the
Financial Markets
10
Financial Markets
• Primary vs. Secondary Markets
• Secondary Markets:
Dealer vs. Auction Markets
- Dealer Market: No physical location
(over the counter OTC)
for example: NASDAQ
-
Auction Market: Physical location
for example: NYSE, AMEX, CBOT
11
“NYSE in the Digital Age”
Sarasota Herald Tribune, Feb 18th, 2007, Page D 1
Traders on the NYSE trading floor
in November 2006.
Traders on a crowded NYSE trading floor in
November 1968
Class Overview:
Principles of Finance
Goal of Financial Manager:
Optimize Shareholders’ Wealth
Three Main Decisions
Long Term
Short Term
Capital Budgeting
Capital Structure
Investing = Spending Money
Financing = Getting Money
Ch 1: Introduction
Ch 2 & 3: Financial Statements,
Ratios, Cash Flows
Ch 5 & 6: Time Value of Money
→ Exam I
Working Capital
Management
Ch 7: Bond Valuation
Ch 8: Stock Valuation
Ch 9: NPV and other
Investment Criteria
Ch 10: Making Capital
Investment Decisions
Ch 12: Capital Market History
Ch 13: Risk, Return and the Capital
Asset Pricing Model
Ch 14: Cost of Capital & WACC
Ch 16: Financial Leverage and
Capital Structure
→ Exam II
→ Cumulative Final Exam
13