alkenes
advertisement

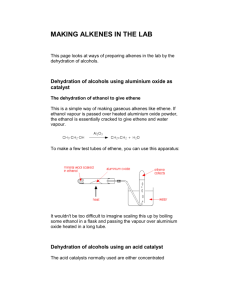
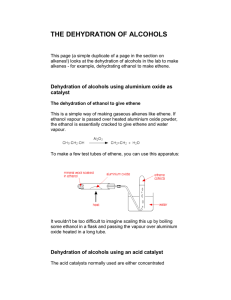
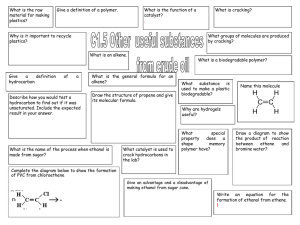
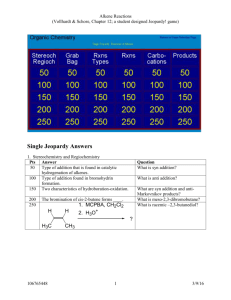
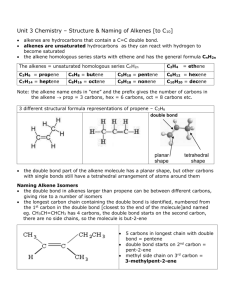
ALKENES Alkenes area class of HYDROCARBONS which contain only carbon and hydrogen. Two other terms which describe alkenes are unsaturated and olefins. UNSATURATED hydrocarbons contain either double or triple bonds. Since the compound is unsaturated with respect to hydrogen atoms, the extra electrons are shared between 2 carbon atoms forming double bonds in alkenes. Alkenes are also called OLEFINS because they form oily liquids on reaction with chlorine gas. The example compounds of ethene or ethylene and pentene are shown on the LEFT. Ethylene is the number one organic chemical synthesized in the U. S. and the world. The small quantities of ethane, propane, and butane found in natural gas are converted into ethene. It can be produced by thermal cracking of ethane to produce ethene and a hydrogen molecule. Alkenes are the raw materials for a number of plastics such as polyethylene, PVC, polypropylene, and polystyrene. Alkene chemistry is found in unsaturated fats, beta-carotene, and seeing light through vision. Structure CnH2n Example: CH2CH2 Properties Physical Properties Boiling points depend on chain length, slightly less than alkanes. Non polar Insoluble in water Less dense than water Chemical Reactivity Alkenes are quite reactive because of the presence of the double bond. Many small compounds react by addition i.e. molecules add to the alkene to form one product. All compounds: Combustion Reaction ALKENE NAMES Root names give the number of carbons in the longest continuous chain. Alkene names are formed by dropping the "ane" and replacing it with "ene" The following list gives samples: Example: root = propane - drop "ane" = "prop" alkene = "prop" + alkene ending = "ene" = propene No. of Root Name Carbons 2 ethene 3 propene 4 1-butene 5 1-pentene Formula CnH2n C2H4 C3H6 C4H8 C5H10 Structure CH2=CH2 CH2=CHCH3 CH2=CHCH2CH3 CH2=CHCH2CH2CH3 The dehydration of ethanol to give ethene This is a simple way of making gaseous alkenes like ethene. If ethanol vapour is passed over heated aluminium oxide powder, the ethanol is essentially cracked to give ethene and water vapour. To make a few test tubes of ethene, you can use this apparatus: It wouldn't be too difficult to imagine scaling this up by boiling some ethanol in a flask and passing the vapour over aluminium oxide heated in a long tube. Dehydration of alcohols using an acid catalyst The acid catalysts normally used are either concentrated sulphuric acid or concentrated phosphoric(V) acid, H3PO4. Concentrated sulphuric acid produces messy results. Not only is it an acid, but it is also a strong oxidising agent. It oxidises some of the alcohol to carbon dioxide and at the same time is reduced itself to sulphur dioxide. Both of these gases have to be removed from the alkene. It also reacts with the alcohol to produce a mass of carbon. There are other side reactions as well, but these aren't required by any current UK A level (or equivalent) syllabus. The dehydration of ethanol to give ethene Ethanol is heated with an excess of concentrated sulphuric acid at a temperature of 170°C. The gases produced are passed through sodium hydroxide solution to remove the carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide produced from side reactions. The ethene is collected over water. WARNING! This is potentially an extremely dangerous preparation because of the close proximity of the very hot concentrated sulphuric acid and the sodium hydroxide solution. I knew of one chemistry teacher who put several students into hospital by getting it wrong! That was many years ago before safety was taken quite so seriously as it is now. The concentrated sulphuric acid is a catalyst. Write it over the arrow rather than in the equation. The dehydration of cyclohexanol to give cyclohexene This is a preparation commonly used at this level to illustrate the formation and purification of a liquid product. The fact that the carbon atoms happen to be joined in a ring makes no difference whatever to the chemistry of the reaction. Cyclohexanol is heated with concentrated phosphoric(V) acid and the liquid cyclohexene distils off and can be collected and purified. Phosphoric(V) acid tends to be used in place of sulphuric acid because it is safer and produces a less messy reaction