ch3 B2 alkenes
advertisement
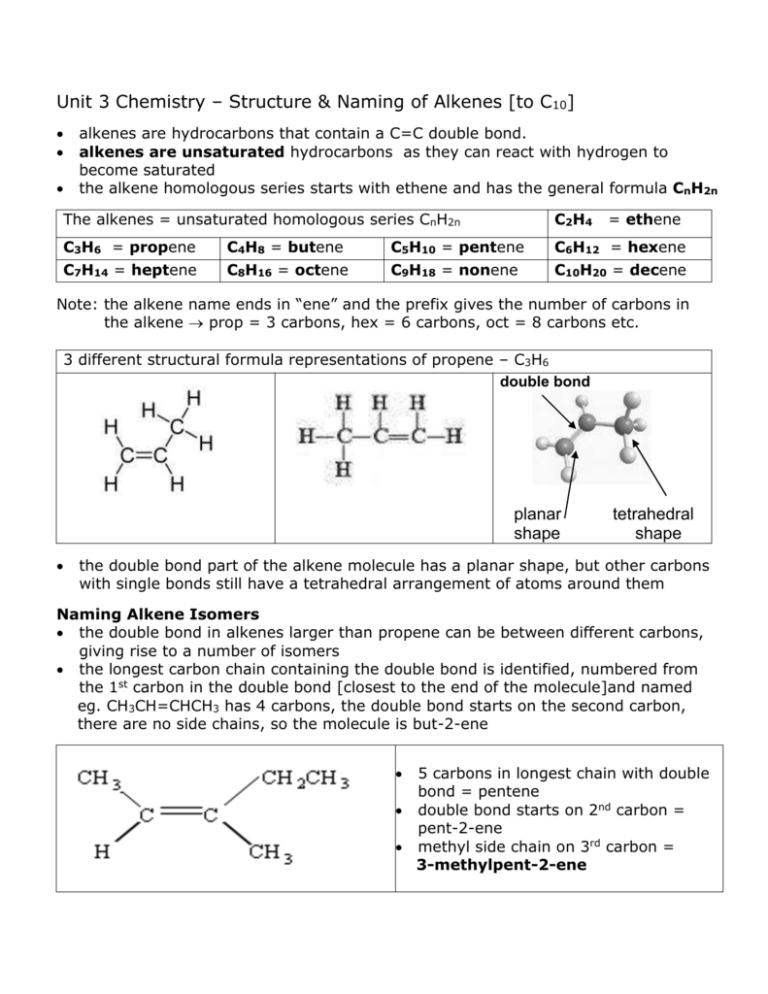
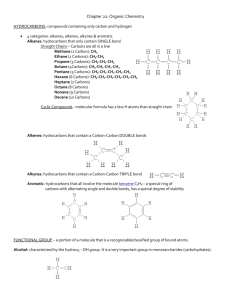
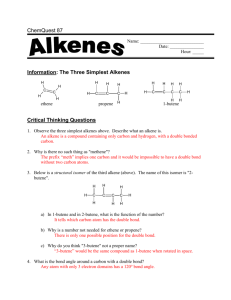
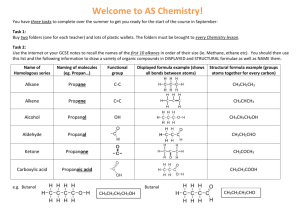
Unit 3 Chemistry – Structure & Naming of Alkenes [to C10] alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain a C=C double bond. alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons as they can react with hydrogen to become saturated the alkene homologous series starts with ethene and has the general formula CnH2n The alkenes = unsaturated homologous series CnH2n C2H4 C3H6 = propene C7H14 = heptene C6H12 = hexene C10H20 = decene C4H8 = butene C8H16 = octene C5H10 = pentene C9H18 = nonene = ethene Note: the alkene name ends in “ene” and the prefix gives the number of carbons in the alkene prop = 3 carbons, hex = 6 carbons, oct = 8 carbons etc. 3 different structural formula representations of propene – C3H6 double bond planar shape tetrahedral shape the double bond part of the alkene molecule has a planar shape, but other carbons with single bonds still have a tetrahedral arrangement of atoms around them Naming Alkene Isomers the double bond in alkenes larger than propene can be between different carbons, giving rise to a number of isomers the longest carbon chain containing the double bond is identified, numbered from the 1st carbon in the double bond [closest to the end of the molecule]and named eg. CH3CH=CHCH3 has 4 carbons, the double bond starts on the second carbon, there are no side chains, so the molecule is but-2-ene 5 carbons in longest chain with double bond = pentene double bond starts on 2nd carbon = pent-2-ene methyl side chain on 3rd carbon = 3-methylpent-2-ene Benzene Rings Benzene [C6H6] is a 6 carbon hydrocarbon arranged in a ring structure, with alternating single and double bonds between the carbons in the ring Equal C–C bond lengths suggest that, rather than alternating single and double bonds, each carbon in the ring is joined to others by single covalent bonds, but also has a delocalised electron that it shares with the others … Different representations of the benzene ring [C6H6] Hydrocarbons containing rings with delocalized electrons are known as aromatic hydrocarbons or arenes. Some important arenes … phenol phenylalanine is an amino acid styrene is the monomer from which polystyrene is made salicylic acid is a precursor in the making of aspirin terephthalic acid is the di-acid used for making polyester acetosalicylic acid [aspirin] Examples involving the Structure and Naming of Alkenes ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------1. Which of the following organic compounds is an alkene? [i] C3H8 [ii] C7H14 [iii] CH3CH=CH2CH3 [iv] C2H4 [v] C2H2 [vi] C5H10 [vii] CH3CH2OH [viii] C10H22 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------2. Copy and complete the following table… Name molecular semi-structural formula formula structural formula ethene propene pent-1-ene 2-methylpropene 3-ethylhex-2-ene ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------3. Draw structural formula and name the 3 structural isomers of butene. ------------------------------------------------------------------------