1 – The Periodic Table - Science at St. Dominics
advertisement

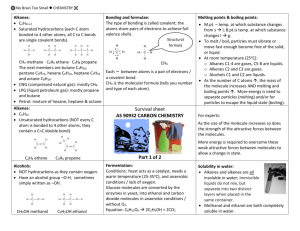
Organic Chemistry 11 – The Alkenes Leaving Certificate Chemistry The Alkenes: CnH2n Ethene: C2H4 2 Carbon Longest Chain Carbon-Carbon double Bond Only H H C H C 2 planar carbons H The Alkenes: CnH2n These are also constituents of crude oil Ethene – C2H4 The first member is 2002 Q. 6 (a) (8) ethene These compounds are not soluble in water The Alkenes: CnH2n Propene: C3H6 3 Carbon Longest Chain Carbon-Carbon double Bond Only H H C C 2 planar carbons H H C H 2005 Q. 4 (i) (6) Tetrahedral carbon H The Alkenes: CnH2n Butene: C4H8 4 Carbon Longest Chain Carbon-Carbon double Bond Only H C H Tetrahedral carbon H H H C C C H H 2 planar carbons H The Alkenes: CnH2n These are also constituents of crude oil Ethene – C2H4 The first member is 2002 Q. 6 (a) (8) ethene These compounds are not soluble in water The Alkenes Functional Group: C = C All of these molecules are unsaturated molecules – They will decolourise bromine water and acidified potassium permanganate solution An unsaturated organic compound is a compound that contains one or more double or triple covalent bonds 2008 Q. 9 (c) (6) Definition 2004 Q. 2 (d) (6) 3 Isomers of C4H8 2008 Q. 9 (b) (12) 2006 Q. 9 (d) (12) Methyl Group H H C H H H 3 H CH 1 2 3 C C C H H 2 – methylprop But – 2 1 - ene – 1 - ene H Isomers of butene But-1-ene But-2-ene 2-methylpropene Preparation of Ethene 2006 Q. 9 (b) (6) Ethanol C2H5OH Aluminium Oxide [catalyst] Al2O3 Ethanol Structural Formulae Ethanol: C2H5OH -OH Group Other Uses 2 Carbon Longest Chain C6H12O6 Glucose Present H H C H 2C2H5OH + 2 CO2 C OH Ethanol Produced in industry by fermentation H H Fuel Solvent Thermometer Balanced Equation H H H H C H C H C H Ethanol C OH Aluminium Oxide H [catalyst] Al2O3 This is an elimination reaction 1.Formation of an unsaturated compound 2.Loss of a small molecule like water H Ethene H2O Water 2007 Q. 8 (a) (6) Preparation of Ethene Balanced Equation for the Synthesis of Ethene C2H5OH Ethanol Al2O3 C 2H 4 Ethene + H 2O Water Preparation of Ethene Aluminium Oxide is placed halfway along the boiling tube Ethanol soaked in glass wool Heating the catalyst using a Bunsen Collecting ethene by the downward displacement of water Preparation of Ethene 2006 Q. 9 (b) (3) 2004 Q. 2 (a) (5) The ethanol is soaked in glass wool with the glass wool being placed in after the ethanol so as to ensure that all of the liquid is soaked up. Preparation of Ethene The first couple of test tubes collected are usually discarded as they contain displaced air from the reaction boiling tube. Preparation of Ethene Be careful of suckback If this occurs: 1. Remove the delivery tube from the boiling tube 2. Apply heat Preparation of Ethene Ethene is Ethene Reaction with acidified potassium permanganate Pink Colourless Ethene Reaction with bromine water Yellow Colourless These tests prove that ethene is an unsaturated compound Preparation of Ethene Ethene is Ethene burns with a luminous flame Burning any hydrocarbon produces carbon dioxide and water vapour Balanced Equation for the Combustion of Ethene C 2H 4 + 3 O2 Turns Limewater Milky 2CO2 + 2 H 2O Turns blue cobalt chloride paper pink The uses of Ethene Ethene is commonly used in industry to ripen fruit and produce the useful plastic polythene Ethene is Chemical Reactions of The Alkenes Addition of Hydrogen Hydrogen Nickel Catalyst Addition The Alkenes e.g. Ethane C2H6 e.g. Ethene C2H4 H The Alkanes H H C C H H H C + C H H2 H Ethene Hydrogen H H Ethane Important Industrial Reaction Used to convert vegetable oils, which are unsaturated, into solid saturated materials used in margarine and dairy products. Addition of Hydrogen H H C C H C H Propene H H H H2 Hydrogen H H H C C C H H H Propane H Addition of Hydrogen H H H H H2 C H C Butene H C C H H H H H H H C C C C H H H H Butane Hydrogen H Uses of hydrogenation reactionsions • Unsaturated fats Saturated fats Addition of Chlorine The Alkenes Ionic Addition Mechanism e.g. Ethene C2H4 H The Chloroalkanes e.g. 1, 2 - Dichloroethane C2H4Cl2 Cl Cl C C H H H C + C H Cl2 H Ethene Chlorine H H 1, 2 - Dichloroethane Important Industrial Reaction 1, 2 – Dichloroethane is used to produce chloroethene which is used to produce the very important plastic PVC 1,2 dichloroethane is used to make PVC Addition of Chlorine H H C C H C H Propene H H H Cl2 Chlorine H H H C C C Cl Cl H 1, 2 -dichloropropane H Addition of Chlorine H H H C C C H C H H Cl2 Chlorine Butene 1, 2 dichlorobutane H H H H H H H C C C C Cl Cl H H H Addition of Bromine Ionic Addition Mechanism H H C + C H Br2 H Ethene Bromine H Br Br C C H H H 1, 2 - dibromoethane Important Industrial Reaction 1, 2 – Dibromoethane is used to prevent poisonous lead accumulating in cars Addition of Bromine H H C C H C H Propene H H H Br2 Bromine H H H C C C Br Br H 1, 2 -dibromopropane H Addition of Bromine H H H C C C H C H H Br2 Bromine Butene 1, 2 dibromobutane H H H H H H H C C C C Br Br H H H Addition of Water Water (Steam) Addition The Alkenes The Primary Alcohols e.g. Ethanol C2H5OH e.g. Ethene C2H4 H H C C H + H Ethene H2O H H H C C H H OH Ethanol Important Industrial Reaction Used to produce the important solvent ethanol Addition of Water H H C C H C H Propene H H H H2O Water 2002 Q. 6 (d) (6) H H H C C C H H H Propanol OH Addition of Water H H H H H2O C H C Butene Butanol H C C H H H H H H H C C C C H H H H Water OH Uses of Hydration reactions Used to make alcohols, which are useful solvents for chemical reactions Addition of Hydrogen Chloride The Alkenes e.g. Ethene C2H4 H The Chloroalkanes Ionic Addition Mechanism e.g. Chloroethane C2H5Cl HCl H C C H + H Ethene HCl H H H C C H H Chloroethane Cl Addition of Hydrogen Chloride H H C C H H H H H C C H Cl Ethene Chloroethane HCl Hydrogen Chloride H Chloroethane – used as a binding agent in paint H Addition of Hydrogen Chloride H H C C H Propene C H H Cl H H H C C C H H H HCl Hydrogen Chloride chloropropane H Addition of Hydrogen Chloride H H H C C C H C H Butene chlorobutane H H H HCl Hydrogen Chloride H H H H H C C C C Cl H H H H Polymerisation of Ethene H H C H H H C Ethene H C H H H H C Ethene H H 2008 Q. 9 (e) (6) C C C C Polythene H H H H n Polymerisation of ethene H H C C H + H H H C C H Ethene H Ethene H H H H C C C C H H H H Polyethene n Important Industrial Reaction Used to produce the very important plastic polythene Polymerisation of Propene H H C H H H C Propene C CH3 H C Propene H H H H C C C C CH3 Polypropene H CH3 H CH3 n Using Polymerisation to make Polyvinylchloride PVC – step 1 H H C C H H Ethene H Cl2 Chlorine H H C C Cl Cl H 1, 2 -dichloroethane Using Polymerisation to make Polyvinylchloride PVC – step 2 H H H C C Cl H C H Cl 1, 2 dichloroethane Cl H C H chloroethene Using Polymerisation to make Polyvinylchloride PVC – step 3 H H Cl C C C H H Cl C H H H H H H C C C C PVC H Cl H Cl n PVC WINDOWS Substitution using UV Light The Alkanes Ethane C2H6 + H2 - H2 The Chloroalkanes Chloroethane C2H5Cl The Alkenes + HCl , + Cl2 Ethene C2H4 + H2O - H2O Aluminium Oxide Catalyst The Polymers Polythene & Polypropene The Alcohols Ethanol C2H5OH