Cholinergic anticholinergic fact sheet
advertisement

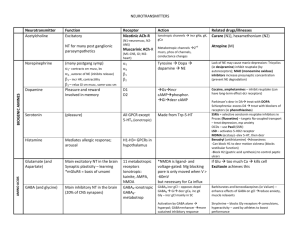
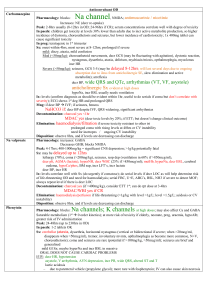
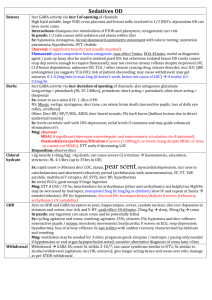
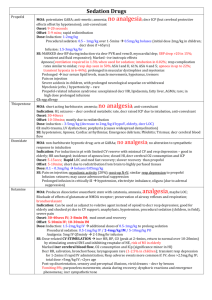
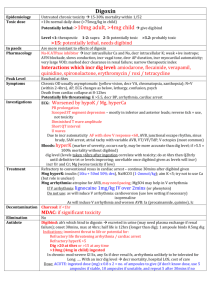
Muscarinic WET Promuscarinics Nicotinic Trt of cholinergic syndrome Anticholingergic / cholinergic syndrome Defecation Urination Meiosis Bronchorrhoea Bradycardia Emesis Lacrimation Salivation Mushrooms (inocybe, clitocybe), OP’s, funnel web venom, betel nut, pilocarpine Fasciculation, tremor, weakness, resp muscle paralysis, incr HR, incr BP; delayed onset weakness nad neurotoxicity Staff protection: gloves, clothing, masks, eye shields, resp filter if INH Decontamination: remove clothing, wash with soap and water (manage off run), use chlorine bleach; charcoal may decr toxicity ABC: start at same time as decontamination; sux may cause paralysis for hrs-days; relative resistance to nondepolarising agents (due to incr Ach at receptor); atracurium is good alternative; high flow O2; diazepam (prevents seizures, may improve survival, reduces resp depression; give 5-10mg IV) Anti-muscarinic Antidotes: Atropine: competitive muscarinic antagonist; reverses cholinergic Sx (non-CNS); no effect on muscle weakness (nicotinic) Indications: wheeze, cough, decr HR, decr BP, miosis, sweating, decr AE Dose: 1-2mg (0.05mg/kg in children) Q5min until drying of secretions, resolution of HR and good AE; may need >2-5mg/hr Glycopyrolate: reverses cholinergic Sx (not CNS); use if atropine run out Dose: 0.05mg/kg IV Pralidoxime: best given within few hrs (before aging), can be given up to 36hrs; onset 10-40mins; reverses some of CNS toxicity (may initially worsen Paralysis, but should reverse NM blockade); hasn’t been shown to improve survival or decr need for ETT; may worsen carbamate poisoning Indications: severe Sx, resistant to atropine Dose: 1-2g slow IV in 200ml 5% dex (25-50mg/kg in children) INF 1g/hr (10-20mg/kg/hr) for 24-48hrs Endpoint: cholinesterase >10%, EMG normalises FFP: increases plasma pseudocholinesterase levels; give 2iu/day until atropine no longer needed Onset 30-120mins resolve in 6-8hrs if mild, 24-60hrs if mod, 7eral days if severe M1 Red as a beat Hot as a hare MOF, rhabdo Dry as a bone, urinary retention, constipation, absent bowel sounds, decr gastric motility (may delay onset) Blind as a bat, mydriasis (often delayed 12-24hrs), cycloplegia Mad as a hatter, confusion, visual hallucinations, seizures, dysarthria H1 Incr HR, hypotension, muscle weakness, postural hypotension, resp paralysis, sedation Antimuscarinics Some have Na and K channel blocking Benztropine (trt of EPSE), antiParkinson drugs Buscopan Atropine, hyoscine, scopolamine, Cyproheptadine, dothiepin, glycopyrolate Antihistamines (most common OD causing toxicity) TCA, SSRI’s, antispasmodics (eg. Carbamazepine) Antipsychotics (eg. Olanzapine, clozapine, phenothiazines, chlorprom) Trt of anticholinergic syndrome Procainamide, quinidine Oxybutynin Ipratropium, tiotropium Trumpet lily, Jimsonweed, amanita muscaria, Belladonna, mandrake Decontamination: Charcoal: may be effective >1hr after due to delayed gastric emptying; MDAC may be used with caution Supportive: Supportive, benzo’s (avoid haloperidol), trt hyperT; NaHCO3 if wide complex tachycardia Physostigmine Antidote: (acetylcholinesterase inhibitor) Indication: if severe CNS toxicity (severe agitation/delirium) esp if not responding to benzos / requiring physical restraint, GHB OD, amanita muscaria 0.1mg Dose: (0.02mg/kg) IV rpt Q5min to 2mg (0.5mg/kg) max; on cardiac monitor CI: co-ingestions with Na blockers, mechanical obstruction of GI/GU tract; QRS >100, PR >200, RAD Relative: asthma, PVD, gangrene, IHD, glaucoma SE: Sx of cholinergic syndrome; seizures, bradycardia and conduction delays with rapid admin Disposition: observe all at least 4hrs