Sedation drugs fact sheet
advertisement

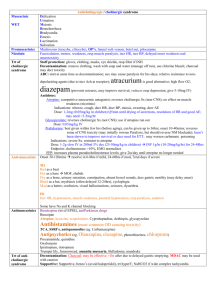
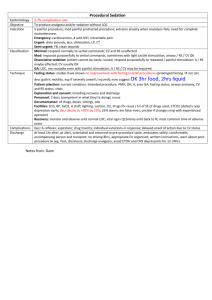
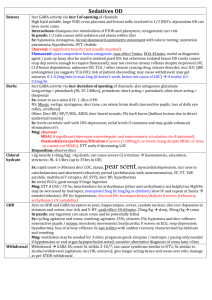
Sedation Drugs Propofol Thiopentone Etomidate Ketamine no analgesia MOA: potentiates GABA; anti-emetic; amnesia; ; decr ICP (but cerebral protective effects offset by hypotension); anti-convulsant Onset: 9-20 seconds Offset: 3-9 mins; rapid redistribution Dose: Induction: 1-2mg/kg Procedural sedation: 0.5 – 1mg/kg over 1-5mins 0.5mg/kg boluses (initial dose 2mg/kg in children; decr dose if >65yrs) Infusion: 1.5-3mg/kg/hr SE: MARKED decr BP during induction via decr PVR and venoD, myocardial dep; SBP drop >20 in 15%; transient and fluid responsive); Marked –ive inotropic effects Apnoea (ventilation required in 1.5% when used for sedation; intubation in 0.02%; resp complication rates similar to midaz; resp dep seen in 50% ASA I and II, 61% ASA 4 and 5; apnoea in up to 22%; transient hypoxia in 6-44%); prolonged in muscular dystrophies and myotonias Prolonged incr serum lipid levels, muscle movements, hypotonus, tremors Pain on injection Severe acidosis in children, with prolonged neurological sequelae on withdrawal Myoclonic jerks / hypertonicity – rare Propofol-related infusion syndrome: unexplained decr HR, lipidaemia, fatty liver, AGMA; rare; in high dose prolonged infusions CI: egg allergy no analgesia MOA: short acting barbiturate; amnesia; ; anti-convulsant Indication: HI, seizures – decr cerebral metabolic rate, decr raised ICP due to intubation, anti-convulsant Onset: 30-40secs Offset: 10-30mins; mostly due to redistribution Dose: induction – 3-5mg/kg (decrease to 2mg/kg if hypoV, elderly, decr LOC) CI: multi-trauma, LV dysfunction; porphyria (causes widespread demyelination) SE: hypotension; Apnoea; Cardiac arrhythmias; Emergence delirium; Phlebitis; Trismus; decr cerebral blood flow no analgesia MOA: non-barbiturate hypnotic drug; acts at GABAa; ; no alteration to sympathetic response to intubation Indication: For induction in pt with limited CV reserve with minimal CV and resp depression – good in elderly; HR unchanged; incidence of apnoea low; closed HI, decr cerebral O2 consumption and ICP Onset: 5-15secs; Rapid LOC and mod fast recovery; slower recovery than propofol Offset: 5-10mins; short due to redistribution from brain to highly perfused tissues Dose: 0.1 – 0.3mg/kg boluses 0.05mg/kg SE: Pain on injection; myoclonic activity (20%); post-op N+V; similar resp depression to propofol Infusion: seizures; may cause adrenocortical suppression Prolonged infusion in critically ill hypotension, electrolyte imbalance, oligura (due to adrenal suppression) analgesia MOA: Produces dissociative anaesthetic state with catatonia, amnesia, , maybe LOC; Blockade of effects of glutamate at NMDA receptor; preservation of airway reflexes and respiration; bronchorelaxant Indication: Can be used as adjunct to volative agent instead of opioid to decr resp depression; good for elderly and shocked pt due to CV support; anaphylaxis, hypotension, procedural sedation (children, in field), severe pain Onset: 30-40secs IV; 3-8min IM; mod onset and recovery Offset: 5-10min IV; 10-30min IM Dose: Induction: 1.5-2mg/kg IV additional doses of 0.5-1mg/kg to prolong sedation Procedural sedation: 0.5-1mg/kg IV / 2-4mg/kg IM / 5-10mg/kg PO Analgesia: 5mg IV Q5minly 2-10mg/hr infusion SE: Dose-related CV STIMULATION incr HR, BP, CO (peak at 2-4mins, return to normal over 10-20mins) by stimulating central SNS and inhibiting reuptake of NE, risk of MI in elderly Marked incr cerebral blood flow, O2 consumption and ICp (significance minor in HI) Decr RR, salivation, bronchorrhoea; laryngospasm rare (1-2.5% in children); transient resp depression for 1-2mins if rapid IV administration; Resp adverse events more common if: IV; dose >2.5mg/kg IV; total dose >5mg/kg IV; <2yrs age Post-op disorientation, sensory and perceptual illusions, vivid dreams – decr by benzos Vomiting 8%; purposeless movements; ataxia during recovery; dysphoric reactions and emergence phenomena;; incr sympathetic tone CI: HI, URTI, LRTI, procedures of post pharynx, CF, <3/12, incr ICP, glaucoma, globe penetration, HTN, CCF, arterial aneurysm, porphyria, thyrotoxicosis, IHD Midazolam Fentanyl Remifentanyl no analgesia MOA: benzo; incr GABAa binding; anxiolytic, sedative, amnesia; ; less hypotension than propofol/thio Onset: 2 mins IV; 15min IM/PR/PO Offset: 30-90mins Dose: 0.05-0.1mg/kg IV in young children 0.025-0.05mg/kg in older children and adults; ie. 2mg stat 1mg increments to 10mg max for anxiolysis for PS in children: 0.5-0.75mg/kg PO, 0.3-0.5mg/kg IN SE: erotic hallucinations at high dose, hypoT, resp dep, paradoxical agitation (1-15% when used PO/IN) Pros: less phlebitis, hypoT than diazepam; less hypotension than propofol / thio Cons: more expensive and longer recovery time than diazepam no amnesia, no anxiolysis MOA: opiate; ; for PSA, combine with sedative agent Indication: hypoV (less hypotensive than thio/propofol/morphine as no histamine release, good in trauma); pain (eg. fractures, burns); good in renal failure Onset: <1 min Peak: 2-5min Offset: 30-60min; tissue uptake and redistribution responsible for termination of effect Dose: Induction: 2-10mcg/kg Analgesia/PSA: 1-2mcg/kg SE: chest wall rigidity (>5mcg/kg, not reversible with naloxone); hypotension (when BP maintained by sympathetic tone); bradycardia; resp depression (outlasts analgesia); N+V; facial pruritis Cons: more expensive than morphine MOA: semi-synthetic opioid; may provide satisfactory intubating conditions with propofol, without paralysis; no amnesia, no anxiolysis Indication: hypoV, pain Onset: 30-180secs Offset: 3-10mins (ultra-short acting) Metabolism: tissue and blood esterases Dose: 0.5mcg/kg; no dose modification in organ failures SE: muscle rigidity, resp depression