Metabolic alkalosis fact sheet
advertisement

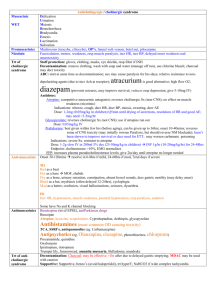
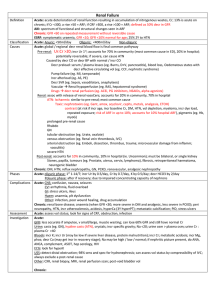
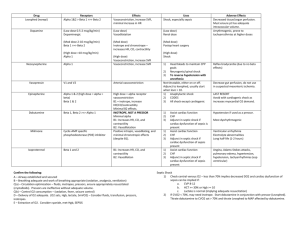
Metabolic Alkalosis RS: shift Oxy-Hb curve to L (incr affinity of Hb for O2 tissue hypoxia); compensatory hypoventilation; blunted resp response to incr CO2 Met: hypoK, hypoCa (causes symptoms), hypoCl dizzy, chest tightness, anxiety, laryngospasm, tremor, carpopedal spasm, Chovstek, Trousseau; decr lactate metabolism stimulates anaerobic glycolysis; incr production of lactic acid and ketoacids CV: arteriolar vasoC NS: incr NH3 entry into CNS hepatic encephalopathy; lethargy, confusion pH 7.55 mortality rate 45% pH 7.65 mortality rate 80% Due to GI / renal loss of acid XS alkali intake Maintenance requires decr ability of kidney to excrete HCO3 (eg. Depletion of Cl) Effects of metabolic alkalosis Causes Chloride sensitive: responds well to N saline Cl and ECV loss hypoV Na reabsorption, K and H excretion hypoCl (urinary Cl <10), hypoK, met alkalosis GI losses (most common cause in ED): Vomit (and pyloric stenosis), NGT drainage, Diarrhoea, Ileostomy, villous adenoma, Cl wasting enteropathy, congenital chloridorrhea Renal losses: post-diuretics (thiazide, loop) Overdose of base (antacids, laxatives) Post-hypercapnia; CF Contraction alkalosis (fluid loss decr renal perfusion incr aldosterone loss of H and reabsorption of HCO3) Chloride insensitive: not responsive to N saline resus No hypoV; urinary Cl >10 Normotensive = Renal losses (Bartter’s, Gitelman’s, active diuretic trt in normotensive patients, severe hypoK/Mg, hyperCa), Refeeding alkalosis Overdose of base (milk-alkalai, massive blood/Hartmann’s transfusion, NaHCO3, Ural) Hypertensive = Renal losses (active diuretic trt in hypertensive patients, Liddle syndrome, RAS, renal failure) Endocrine (hyperaldosteronism, adrenal Ca, adrenal hyperplasia, Cushings, exogenous steroids, renin secreting tumour, licorice, chewing tobacco) Compensation Mng Expected PaCO2 = (0.9 x HCO3) + 9 Compensation may not be found if: pain, hyperV due to pul congestion/hypoxaemia If change in PaCO2 = change in HCO3, there is appropriate resp compensation If PaCO2 too high, there is additional resp acidosis If PaCO2 too low, there is additional resp alkalosis Trt underlying cause; improve renal HCO3 excretion; O2; correct electrolyte imbalance; acetazolamide 250mg BD; HCl rarely required If vol deplete / Cl sensitive give IVF If vol overloaded / Cl insensitive give spironolactone Notes from: METABOLIC ALKALOSIS: (PC02 > 45, HCO3- , B.E. > +2) Volume Depleted Normal Volume or Volume Overload (Urinary Cl < 10mmol/L) (Urinary Cl > 15mmol / L) 1. Upper GIT losses. 2. Renal: Diuretics. Exception, current diuretic treatment Cl is Recently ceased diuretics Cl is 3. Skin loss (of NaCl) 1. Hyperaldosteronism 2. Cushings 3. Rare: Bartter’s syndrome. Severe K+