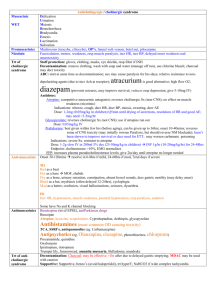
Interactions which incr dig level
advertisement

Digoxin Epidemiology Toxic dose Untreated chronic toxicity 15-30% mortality within 1/52 >10x normal daily dose (>75mcg/kg in child) Potentially lethal: >10mg Level <1: therapeutic adult, >4mg child give digibind 1-2: supra 2-3: potentially toxic >15: potentially lethal, needs digibind In paeds Pharmacology >3.2: probably toxic Are more resistant to effects of digoxin Na-K ATPase inhibitor incr intracellular Ca and Na, decr intracellular K; weak +ive inotrope; AVN blockade, slows conduction, incr vagal tone, decr AP duration, incr myocardial automaticity; very large VOD; marked decr clearance in renal failure; narrow therapeutic index Interactions which incr dig level: amiodarone, flecainide, verapamil, quinidine, spironolactone, erythromycin / roxi / tetracycline Peak Level Symptoms Reached at 6hrs Chronic OD usually asymptomatic (yellow vision, decr VA, chromatopsia, xanthopsia); N+V (within 2-4hrs), AP, ECG changes as below, lethargy, confusion, psych Death from cardiac collapse at 8-12hrs Potentially life threatening: K >5.5, decr BP, arrhythmia, cardiac arrest Investigations ECG: Worsened by hypoK / Mg, hyperCa PR prolongation Scooped ST segment depression – mostly in inferior and anterior leads; reverse tick = use, not toxicity Diminished T wave amplitude Short QT interval U waves Due to incr automaticity AF with slow V response <60, AVB, junctional escape rhythm, sinus brady, SAN arrest, atrial tachy with variable AVB, VT/VF/TdP, V ectopics (most common) Bloods: hyperK (marker of severity, occurs early, may be more accurate than dig level; if >5.5 = 100% mortality without digibind) dig level (levels taken >6hrs after ingestion correlate with toxicity; do at 4hrs then Q2hrly until definitive trt or levels improving; unreliable once digibind given as levels will incr) incr Ur and Cr; Mg (worse toxicity if low) Treatment Refractory to conventional resus in cardiac arrest – continue 30mins after digibind given Mng hyperK: insulin (10iu + 50ml 50% dex), NaHCO3 (1-2mmol/kg); aim K <5; try not to use Ca (but role is unclear) Mng arrhythmia: atropine for AVB, may need pacing; MgSO4 may help in V arrhythmia If V arrhythmia: lignocaine 1mg/kg IV over 2mins (or phenytoin) Do not use: as will induce V arrhythmia: cardioversion (use low setting if necessary) isoprenaline As will induce V arrhythmia and worsen AVB: Ia (procainamide, quinine), Ic Decontamination Charcoal: if <1hr MDAC: if significant toxicity Elimination Antidote No Digibind: ab’s which bind to digoxin excreted in urine (may need plasma exchange if renal failure); onset 30mins, max at 4hrs; half life is 12hrs (longer than dig); 1 ampoule binds 0.5mg dig Indications: imminent threat to life or potential for: Refractory life threatening arrhythmia / cardiac arrest Refractory hyperK >5 Dig >20 at 6hrs or >15 at any time >10mg (4mg in child) ingested In chronic: mod-severe GI Sx, any Sx if decr renal fx, arrhythmia unlikely to be tolerated for Long …. With an incr dig level decr mortality, hospital LOS, cost of care Dose: ACUTE: ingested dose (mg) x 0.8 x 2 = no. of ampoules to give (if don’t know dose, use 5 ampoules if stable, 10 ampoules if unstable, and repeat 5 after 30mins if no Disposition response; give 20 ampoules in cardiac arrest) CHRONIC: (dig level (mmol/L) x weight (kg)) / 100 = no. of ampoules to give (usually need 2 ampoules if no response at 30mins, give further 2) Dilute dose in 100ml N saline and give over 30mins 40mg/ampoule = decr dig level by 1 = binds 500mcg dig SE: occurs in <5%; rebound hypoK, allergy rare, may get AF, exac of CCF due to loss of inotropic action Monitor 6hrs (from presentation / digibind administration); then can discharge if no GI Sx, normal K, normal dig levels, normal ECG Chronic usually requires admission