Naming Compounds
advertisement

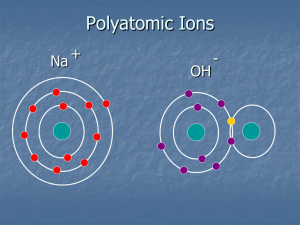
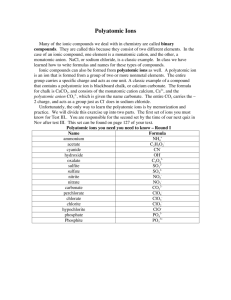
Naming Compounds Ionic Compounds • The net (final) charge of the compound will be ZERO! • This means that there must be equal amounts of positive and negative charges – not necessarily always equal charges on the ions. Naming ions • Metal ions have their original name • Metals with multiple oxidation numbers (possible charges) will need to include the specific oxidation number – Iron (II) or Tin (IV) • Non-metals keep the same base name, but change the ending to “ide” – Chlorine becomes chloride – Sulfur becomes sulfide Practice Naming • • • • • • • • KCl potassium chloride Mg3N2 magnesium nitride CuI Copper (I) iodide (copper has +1 charge) FeO Iron (II) oxide (iron has +2 charge) Writing Chemical Formulas • Total Charge must equal zero • If there is only one of the atom, not subscript number is given - NaCl • Formulas are typically written in reduced form (H2O not H12O6) • Shortcut – sometimes you can simple take the ion charges and put them as the subscripts of the other elements – Fe+3 + O-2 -> Fe2O3 Practice Writing Formulas • • • • • • • • magnesium chloride Mg+2 + Cl -1 -> MgCl2 sodium phosphide Na+1 + P-3 -> Na3P barium nitride Ba+2 + N-3 -> Ba3N2 copper (II) iodide Cu+2 + I-1 -> CuI2 Polyatomic Ion Names • • • • • • • • • • Ammonium Sulfate Carbonate Nitrate Chlorate Cyanide Bicarbonate Hydroxide Peroxide Phosphate NH4+1 SO4-2 CO3-2 NO3-1 ClO3-1 CN-1 HCO3-1 OH-1 O2-2 PO4-3 Naming with Polyatomic Ions • Metals are named as usual • Polyatomic ions use their specific names – – – – NO3 – nitrate NO2 – nitrite OH – hydroxide SO4 – sulfate • Name simply combines ion names – MgSO4 is magnesium sulfate • If more than one polyatomic ion is needed, it is put in parenthesis and given a subscript – Mg(OH) is magnesium hydroxide (two hydroxides needed) Practice Writing Names with Polyatomic Ions • • • • • • • • KClO3 potassium chlorate Mg(NO3)2 magnesium nitrate Na2SO3 sodium sulfite Fe2(CO3)3 Iron (III) carbonate (iron has +3 charge) Practice Writing Formulas • • • • • • • • magnesium phosphate Mg+2 + PO4-3 -> Mg3(PO4)2 sodium peroxide Na+1 + O2-2 -> Na2O2 ammonium nitride NH4+1 + N-3 -> (NH4)3N copper (II) hydroxide Cu+2 + OH-1 -> Cu(OH)2