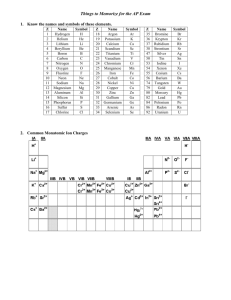
1.Covalent bonding – polar and non-polar a. Definition b. Recognize
advertisement

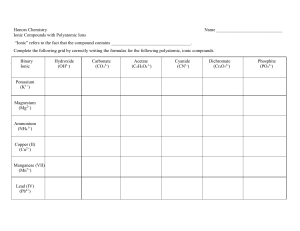
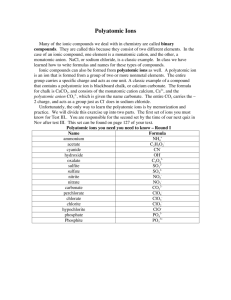
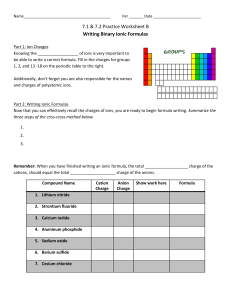
C H E M -1 0 0 0 S tud y S he e t – E x a m # 2 1.Covalent bonding – polar and non-polar a. Definition b. Recognize each from atoms in bond c. Definition of double and triple bonds 2. Predicting ionic compound formulas – both binary and those involving polyatomic ions 3. Polyatomic ion list (9 ions) – name, formula and charge 4. Naming binary ionic compounds and ionic compounds with polyatomic ions 5. Polar and non-polar molecules – recognize from formula 6. Recognize balanced and unbalanced chemical equations 7. Avogadro’s # 8. Molecular mass calculation from compound formula 9. Mole a. Definition b. Conversion between number of moles and mass in grams 10. Stoichiometry or mole relationships from balanced chemical equations 11. Solutions a. Definition b. Solvent and solute identities 12 Solubility 13 Molarity and % Concentration (both by volume and by weight) 14. Intermolecular attractions a. Dipole b. London or Dispersion – Understand that larger molecules have greater attractions c. Hydrogen bonding (definition and strength) d. Solids, liquids and gases based on strength of attractions 15. Acids and bases a. Definitions – Arrhenius and Bronsted-Lowry b. Properties c. Recognize in a chemical equation d. Strong and weak – definitions and list of strong e. Neutralization and definition of salt f. pH and pOH calculations and determination of acidity and basicity g. Antacids and why they work h. Acidosis and alkalosis 16. Phase Changes: a. Know names and meanings (melting, freezing, vaporization, condensation and sublimation