Carbon Compounds
advertisement

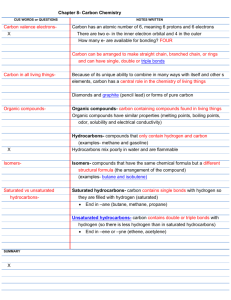
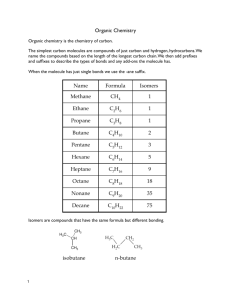
Carbon Compounds Organic compounds A compound that contains carbon. “organic” means “of living things” – Can occur naturally: – Wood, paper – Produces artificially also: – Plastics, fuels, cleaning solutions Organic Compounds Many have low melting points and low boiling points – Causes them to be liquids and gases at room temperature Liquids generally have a strong odor Do NOT conduct electricity Do NOT dissolve well in water Hydrocarbons The simplest organic compound. Hydrocarbons contain only the elements hydrogen and carbon. Examples: methane, propane, butane Hydrocarbons Properties: – ALL are flammable – When burned a large amount of energy is released – Mix poorly with water Hydrocarbons Simplest hydrocarbon is methane (CH4) Ethane – C2 H6 Propane – C3 H8 These are the molecular formulas – Create the structural formulas. Structural Formula Shows the kind, number and arrangement of atoms in a molecule. Isomers – Compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structures. – Each isomer is a different substance. Show Structural Formula Molecular Formula –Methane CH4 –Ethane C2H6 –Propane C3H8 Structural Formulas Hydrocarbons with 4 or more carbon atoms can have straight or branched arrangements. Structural Formula Butane C4H10 – Straight Chain – Branched Chain Double or Triple Bonds Two carbon atoms can form single, double or triple bonds Bonds beyond triple bonds do not exist in nature. Hydrocarbons Saturated Hydrocarbons – (single bonds) carbon is “saturated” or filled up with hydrocarbons – Ends in -ane Unsaturated Hydrocarbons – (double and triple bonds) have fewer hydrogen atoms for each carbon compared to saturated hydrocarbons – Ends in –ene or -yne Unsaturated Hydrocarbons Ethene – C2H4 – Simplest double carbon bond – Produced by bananas Ethyne – C2H2 – Simplest triple carbon bonds – acetylene Substituted Hydrocarbons Atoms of other elements replace one or more hydrogen atoms in a hydrocarbon Halogen compounds Alcohols Organic acids Halogen Compounds Trichloroethane – C2H3Cl3 Perchloroethylene – C2H2Cl2 Alcohols -OH substituted for hydrogen atom in a hydrocarbon -OH called hydroxyl group An alcohol contains one or more hydroxyl groups Alcohol Methanol – CH3OH Ethanol – One hydrogen atom from ethane, C2H6, plus one hydroxyl group – C2H5OH Organic Acids A substituted hydrocarbon that contains one or more carboxyl groups – -COOH – Acetic Acid – main compound in vinegar CH3COOH – Formic Acid – stinging from ants HCOOH Esters Alcohol + Organic Acid Esters have: Ester – Pleasant fruity smells – Ingredient in medications (ASA, … ) Polymers A very large chain of molecules made of chains of many smaller molecules. Monomers – smaller molecules Polymers Natural Polymers – Wool made by sheep – Cotton plants make cotton – Silk worms make silk Synthetic Polymers – Manufactured, or synthesized, in factories – Polyester, nylon, plastics Saturated, Unsaturated, or substituted hydrocarbon? H H C H OH Saturated, Unsaturated, or Substituted Hydrocarbons? H H H C C H H H C H C H H H Saturated, Unsaturated, or Substituted Hydrocarbon? H H C H OH Saturated, Unsaturated, or Substituted Hydrocarbon? H H Cl C C H Cl Cl Saturated, Unsaturated, or Substituted Hydrocarbon? H H C H C H Saturated, Unsaturated, or Substituted Hydrocarbon? H H C H COOH