Organic Chemistry
advertisement

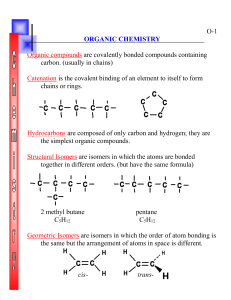
Name______________________________________________ Honors Chemistry Reading Guide Organic Chemistry (Chapter 22) Section 1: Organic Compounds Define the following terms: organic compound: hydrocarbon: isomers: What is catenation? How does it help to contribute to the diversity of organic compounds? How are isomers similar to each other? In what way are isomers different? How are structural formulas useful for illustrating organic isomers? In what way are they lacking information? Can hydrocarbons with only single bonds have geometric isomers? Why or why not? Section 2: Hydrocarbons Define the following terms: saturated hydrocarbons: homologous series: cycloalkane: alkyl group: unsaturated hydrocarbon: aromatic hydrocarbons: What do the terms saturated and unsaturated mean when applied to hydrocarbons? What is the fewest number of carbons needed for an alkane to have structural isomers? As the number of carbon atoms increases, what happens to the number of possible structural isomers? *****CAREFULLY read the section Organic Compounds have systematic names!! This will help you to understand the basis for much of this unit! Using Figure 2.4, what do you notice about the trend in boiling point for straight-chain hydrocarbons? Explain this in terms of the intermolecular forces of attraction. Draw the structural formula of benzene and the “shorthand” formula. What group of hydrocarbons have benzene as a basis for their structure? Give the CORRECT name for the following hydrocarbons: a. 1-methyl propane b. 2-ethyl butane Draw and name the three isomers with the formula C5H12. Section 3: Functional Groups Define the following terms: functional groups: Write the general formula for a. alcohol b. ether c. alkyl halide d. aldehyde e. ketone f. carboxylic acid g. ester h. amine Based on the boiling points of water and methanol, which would you expect to have a greater degree of hydrogen bonding? Explain your answer. Aldehydes and ketones have the same functional groups. Why are they classified as separate classes of organic compounds? How are esters related to carboxylic acids? Section 4: Organic Reactions Define the following terms: polymer: monomer: Compare substitution and addition reactions. What type of reaction would you expect between 2-octene and hydrogen bromide? Can an addition reaction occur between ethane and bromine? Why or why not? In a chemical reaction, two small molecules are joined and a water molecule is produced. What type of reaction took place? What is the structural requirement for a molecule to be a monomer in an addition polymerization reaction?







![LC Fuels and Thermochemistry [PDF Document]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008241147_1-6ebc9d449a7896c353ddca434fe5df53-300x300.png)