Chemistry Homework Answer Key: Hydrocarbons & Catenation
advertisement

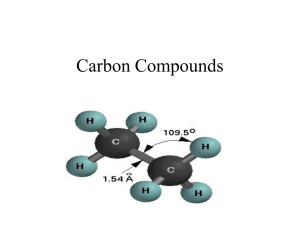
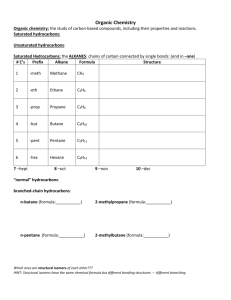
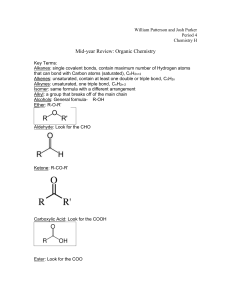
Homework: pg 741 (1,5,6a,6c, 7, 8, and 10) Answer Key 1. a. What is catenation? a. Catenation is the covalent binding of an element to itself to form chains or rings. b. How does catenation contribute to the diversity of organic compounds? b. Catenation contributes to the diversity of organic compounds by allowing carbon atoms to bond together in many possible arrangements. 5. What are hydrocarbons, and what is their importance? Hydrocarbons are molecules composed of hydrogen and carbon. They are important because they are the backbones of other organic compounds. 6a. What do the terms saturated and unsaturated mean when applied to hydrocarbons? A saturated hydrocarbon has as many hydrogen atoms as possible, with only single covalent bonds to every carbon atom. An unsaturated hydrocarbon does not have as many hydrogen atoms because not all carbon atoms have four single covalent bonds. 6c. Classify alkenes, alkanes, alkynes, and aromatic hydrocarbons as either saturated or unsaturated. Alkanes are saturated. Alkenes, alkynes, and aromatic hydrocarbons are unsaturated. 7. Classify each of the following as an alkane, alkene, alkyne, or aromatic hydrocarbon. a. aromatic hydrocarbon b. alkene c. alkyne d. alkane 8. Give the general formula for the members of the following: a. alkane series CnH2n+2 b. alkene series CnH2n c. alkyne series CnH2n−2 10. What are cycloalkanes? Cycloalkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain ring structures.