Link for Period 2
advertisement

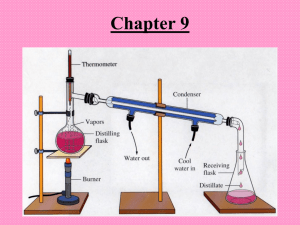
ORGANIC COMPOUNDS ORGANIC COMPOUNDS ARE THE C O M P O U N D S T H AT C O N T A I N CARBON THEY CAN BE FOUND IN PRODUCTS MADE FROM LIVING THINGS OR T H I N G S T H AT A R E A R T I F I C I A L LY PRODUCED. T H E Y A R E P A R T T H E S O L I D M AT T E R OF EVERY ORGANISM ON EARTH. R A W M AT E R I A L S F O R M O S T M A N U FAC T U R E D O RG A N I C COMPOUNDS COME FROM PETROLEUM OR CRUDE OIL. M A N Y O RG A N I C C O M P O U N D S H AV E SIMILAR PROPERTIES IN TERMS OF H A V I N G M E LT I N G P O I N T S , B O I L I N G POINTS, ODOR, ELECTRICAL C O N D U C T I V I T Y, A N D S O L U B I L I T Y. M A N Y H A V E L O W M E LT I N G A N D L O W BOILING POINTS T H E Y T E N D TO H AV E ST RO N G ODORS DON’T CONDUCT ELECTRIC CURRENT A N D D O N ’ T D I S S O LV E I N W AT E R . CARBON COMPOUNDS BY Lily, Jorge, and Skyler Carbon Atoms Carbon atoms act as the backbone of a skeleton or the molecules of these compounds. Carbon compounds include gases such as, propane; liquids such as, olive oil; and solids such as, cotton. Mixtures of compounds can be found in food, paper, and shampoo. organic compounds organic compounds are compounds that contain carbon. the term is used because scientists once thought that organic compounds could only be produced by living things. but, now scientists know that they can also be artificially produced. many organic compounds have similar properties in terms of melting points, boiling points, odor, electrical conductivity, and solubility. many organic compounds have low melting points and low boiling points. as a result they have strong odors. hydrocarbons the simplest organic compounds are hydrocarbons. a hydrocarbon is a compound that only contains hydrogen and carbon. Methane, the main gas in natural gas, and it is used to heat homes Propane STRUCTURE OF HYDROCARBONS By: Athena the awesome Caden the grey Marleen the sparkles CARBON CHAINS A hydrocarbon may be straight, branched or ring shaped They can be straight or branched STRUCTURE FORMULA A structure formula shows the kind, number and arrangement of atoms in a molecule. METHANE CH 4 ETHANE C 2 H 6 PROPANE C 3 H 8 Compound that have the same chemical formula but different structural formulas. Butane and Isobutane Double and Triple bonds Carbon can form a single or double bond with oxygen Structural formulas represent a double bond with a double dash between two elements A triple bond is indicated by a triple dash Saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons By Andrew Martin Penny Kibbe Jaquie Macias Contents Saturated Hydrocarbons Unsaturated Hydrocarbons Classifying Saturated Hydrocarbons Classifying Unsaturated Hydrocarbons ConclusionS Saturated Hydrocarbons Saturated Hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons (molecules with only Hydrogen and Carbon Atoms) in which all bonds are single bonds It has the maximum number of atoms in the valence field All saturated hydrocarbons end in the suffixes –ane Unsaturated Hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons in which at least one or more bonds are double or triple All unsaturated hydrocarbons end in the suffix –ene or –yne. Simplest unsaturated Hydrocarbon and Function The simplest unsaturated hydrocarbon with one double bond is ethene (C2H4) Fruits produce ethene gas because it helps the fruit ripen. The simplest hydrocarbon with one triple bond is ethyne (C2H2), also known as acetylene. Acetylene torches are used for welding. Conclusion Saturated Hydrocarbons Unsaturated Hydrocarbons Classifying Saturated Hydrocarbons Classifying Unsaturated Hydrocarbons Conclusion Substituted Hydrocarbons And compounds containing halogens • Hydrocarbons contain only one carbon and one hydrogen • Carbon can form stable bonds with several other elements • Substituted hydrocarbon- atoms of other elements replace one or more hydrogen atoms in a hydrocarbon • Hydrocarbons include- halogen-containing compounds, alcohols, and organic acids • One or more halogen atoms replace hydrogen atoms • Halogen family includes fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine • Freon is used as a cooling liquid in refrigerators and air conditioners Chapter 8 Stuff By: Pierson, Caius, Joe Substituted Hydrocarbons • Substituted Hydrocarbons are where atoms of other elements replace one or more hydrogen atoms in a hydrocarbon. • If you change on hydrocarbon it becomes a completely different compound. • The carbon can bond with many other elements like oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens Compounds Containing Halogens • In some substituted hydrocarbons one or more halogens replace hydrogen atoms. • Halogen family includes fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine. • Freon is used as a as a cooling agent in refrigerators. Alcohols • An alcohol is a substituted hydrocarbon that contains one or more hydroxyl groups. • They have high boiling points and dissolve well in water • When a hydroxyl group is substituted for one hydrogen atom in ethane, the result is ethanol. • Ethanol is produced naturally by the action of yeast or bacteria on the sugar stored in corn. Organic Acids • An organic acid is a substituted hydrocarbon that contains one or more carboxyl groups. • A carboxyl group is written as –COOH • You can find organic acids in many foods Esters • An ester is a compound made by chemically combining an alcohol and an organic acid. • Many esters smell like fruit • Esters are responsible for the smell of many fruits • Some esters are used in medicines like aspirin * By: Jack, Ruysch, and Max * In chapter 8, our science textbook explains carbon compounds. Organic compounds are compounds that contain carbon within them. It also talks about hydrocarbon, isomers, the carboxyl group, monomers, and so on. * * An ester is a compound made by chemically combining alcohol and an organic acid. * * Very large molecules made of a chain of smaller molecules bonded together is a polymer. The prefix poly means “many” and mono means “one”. * * Some polymers are made by many living things. Examples are sheep growing wool and cotton fibers from cotton seeds. Synthetic polymers are made in factories. Nylon or polyesters are synthetic polymers. *