Window Cleaners Effects on Euglena Algae
advertisement

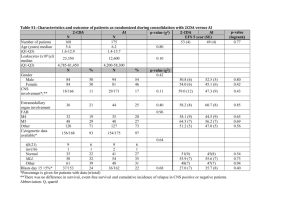
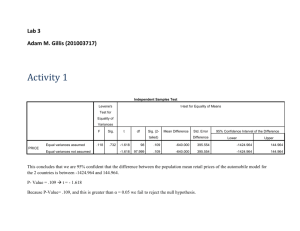
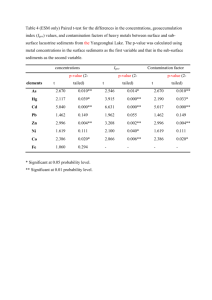
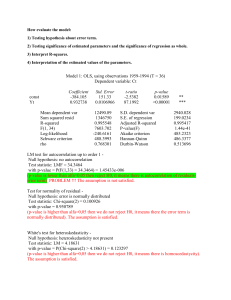
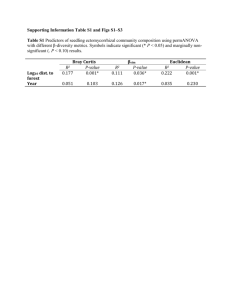
Window Cleaners Effects on Euglena Algae John Wearden Grade 9 Central Catholic High School Window Cleaners Include any chemical used as a cleaning product intended for use on a surface May include chemicals that are potentially toxic May runoff and harm organisms Long term effects, unclear Eutrophication Caused by an overabundance of nutrients in an ecosystem No limiting factor on algae populations Uncontrollable growth takes up resources for other organisms-oxygen Limits biodiversity Can occur naturally Windex Active Ingredients 2-Hexoxethanol Chemical Formula C8H18O2, coalescing agent, can cause depression and kidney failure, severe irritant Ammonium Hydroxide Chemical Formula NH4OH Can cause breathing complications if inhaled Giant Eagle Window Cleaner Active Ingredients Ammonia NH3, if inhaled can lead to lung damage and death Glycol Ether Can cause severe liver and kidney damage, as well as fatigue, lethargy, and anorexia with chronic exposure. Green Shield Active Ingredients Acetic Acid - CH3COOH, mild irritant Algae Large diverse group of simple, and usually autotrophic organisms Basis of the aquatic food chain Used as as a bio-indicator for aquatic environments Euglena gracilis Algal - like protist Survives in both fresh and salt water Performs photosynthesis and endocytosis Becomes dormant in negative conditions No cell wall Common experimental model Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Flagellated, unicellular green algae Commonly found in fresh water Generally light sensitive Common experimental model No cell wall Purpose To determine the effects various window cleaners have on algae To examine the effects of window cleaners on algal population density Hypothesis Null Hypothesis: The window cleaners will not significantly affect algal or survivorship Alternative Hypothesis: The window cleaners will significantly affect algal survivorship Materials micro pipette (1000µL) tips for micro pipette 30 test tubes (borosilicate 13x100mm) 4 tube racks 45 mL euglena gracilis 45 mL chlamydomonas reinhardtii 84 mL spring water 90 mL of soil water 7 mL Windex window cleaner 7 mL Giant Eagle window cleaner 7 mL Green Shield window cleaner Carolina spectrophotometer wax paper large window Procedure 1. 2. Created a stock solution of 10% and 1% for each window cleaner. Window cleaners, algae, spring water, and soil water were used to create the following solutions. 1% .1% .01% .001% and 0%. Solution Table 0 .001 .01 .1 1 Algae 1 1 1 1 1 Variable 0 .05 .5 .05 .5 Spring Water 3 2.95 2.5 2.95 2.5 Soil Water 1 1 1 1 1 Procedure (continued) 3. Tubes were placed in racks recieving equal sunlight from the same window. 4. Every other day absorbance reading were taken using a spectrophotometer set at 430nm. Statistical Analysis ANOVA Compares variation within groups to variation between groups. If a p-value is less than the alpha .05 it suggests that the null hypothesis can be rejected. Dunnett’s Test Compares each experimental group to the control group individually Each experimental group is then compared to t-crit value of 3.5 Day 6: P-value .002 Day 14: P-value .003 above alpha .05 Day 6: P-value .0001 Day 14: P-value .018 above alpha .05 Day 6: P-value .006 Day 14: P-value .173 above alpha .05 Day 6: P-value .568 Day 14: P-value .003 above alpha .05 Day 6: P-value: .004 Day 14: P-value: .006 above alpha .05 Day 6: P-value .544 Day 14: P-value .868 Dunnett’s Test Euglena Windex Euglena Giant Eagle Euglena Green Shield Chlamydom onas Windex Chlamydom onas Giant Eagle Chlamydom onas GreenShiel d Day 6 4.37285 sig 3.49276 sig 2.60912 (did not have an alpha of .05) 3.38217 sig (did not have an alpha of .05) Day 14 5.67261 sig 3.28561 sig (did not have an alpha of .05) 4.30152 sig 3.26012 sig (did not have an alpha of .05) Alpha: 3.05 Conclusion Accept the alternative hypothesis for the Windex cleaner and Giant Eagle cleaner. All were determined as having significant long term effects. Reject the alternative hypothesis for the Green Shield cleaner None were determined to have significant long term effects Limitations and Extensions Limitations The growing period occurred during the middle of December, different effects may rise with more sunlight Extensions Further chemicals can be isolated to determine which causes the effect or which combination causes the effect. More diverse species could have been used to better model an ecosystem More replicates could be used to nullify any outliers References http://www.epa.gov/ http://www.windex.com/ http://www.gianteagle.com/ http://www.ewg.org/ http://www.britannica.com/ http://www.nlm.nih.gov/