Sample Problems for Chapter 14
advertisement

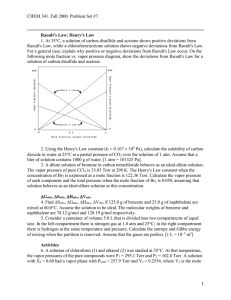
Sample Problems – Chapter 14 Some useful constants: solvent Acetic acid Benzene Chloroform Naphthalene Water normal boiling point, °C Kb, °C/m freezing point, °C Kf, °C/m 118.9 80.1 61.2 – 100.0 3.1 2.53 3.63 – 0.512 16.6 5.5 – 80.22 0.00 3.9 5.12 – 6.85 1.86 1. What is the mole fraction of H2 in a gaseous mixture containing 1.0 g H2, 8.0 g O2, and 16 g CH4? 2. Determine the mole fractions of both substances in a solution containing 36.0 g water and 46.0 g glycerin, C3H5(OH)3. 3. A solution contains 10.0 g acetic acid, CH3COOH, in 125 g water. What is the concentration of the solution expressed as (a) mole fractions of CH3COOH and H2O; (b) molality of CH3COOH? 4. Calculate the molalities and the mole fractions of acetic acid in two solutions prepared by dissolving 120 g acetic acid (a) in 100 g water; (b) in 100 g ethyl alcohol, C2H5OH. 5. Calculate the molality of a solution containing: (a) 0.65 mol glucose, C6H12O6, in 250 g water; (b) 45 g glucose in 1.00 kg water; (c) 18 g glucose in 200 g water. 6. How many g CaCl2 should be added to 300 mL water to make up a 2.46 m solution? 7. Calculate the molarity, molality, and mole fraction of ethyl alcohol, C2H5OH, in a solution of total volume 95 mL prepared by adding 50 mL ethyl alcohol (density = 0.789 g/mL) to 50 mL water (density = 1.0 g/mL). 8. The density of 10.0% by mass KCl solution in water is 1.06 g/mL. Calculate the molarity, molality, and mole fraction of KCl in this solution. 9. The vapor pressure of pure liquid solvent A is 0.80 atm. When a nonvolatile substance B is added to the solvent, its vapor pressure drops to 0.60 atm. What is the mole fraction of component B in the solution? 10. The vapor pressure of pure water at 26°C is 25.21 torr. What is the vapor pressure of a solution which contains 20.0 g glucose, C6H12O6, in 70 g water at the same temperature? 11. The vapor pressure of pure water at 25°C is 23.76 torr. The vapor pressure of a solution containing 5.40 g of a nonvolatile substance in 90.0 g water is 23.32 torr. Compute the molecular weight of the solute. 12. At 30°C, pure benzene, C6H6, has a vapor pressure of 121.8 torr. Dissolving 15.0 g of a nonvolatile solute in 250 g of benzene produced a solution having a vapor pressure of 120.2 torr. Determine the approximate molecular weight of the solute. 13. The vapor pressure of water at 28°C is 28.35 torr. Compute the vapor pressure lowering at 28°C of a solution containing 68 g of cane sugar, C12H22O11, in 1000 g of water. 14. What is the freezing point of a 10% (by weight) solution of CH3OH in water? 15. When 10.6 g of a nonvolatile substance is dissolved in 740 g of ether, its boiling point is raised by 0.284°C. What is the molecular weight of the substance? For ether Kb = 2.11 °C/m. 16. The freezing point of a sample of naphthalene was found to be 80.6°C. When 0.512 g of a substance is dissolved in 7.03 g naphthalene, the solution has a freezing point of 75.2°C. What is the molecular weight of the solute? 17. How much ethyl alcohol, C2H5OH, must be added to 1.00 L of water so that the solution will not freeze at –20°C? 18. If the radiator of an automobile contains 12 L of water, how much would be the freezing point lowered by the addition of 5 kg of Prestone (glycol, C2H4(OH)2)? 19. An aqueous solution containing 288 g of a nonvolatile compound in 90.0 g of water boils at 101.24°C at 1.00 atm pressure. What is the molecular weight of the compound? 20. A solution containing 3.24 g of a nonvolatile compound and 200 g of water boils at 100.130°C at 1 atm. What is the molecular weight of the solute?