Chapter 11 Properties of Solutions
advertisement

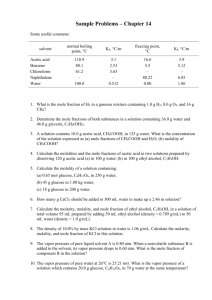
Chapter 11 Properties of Solutions Definitions: Solute: Solvent: A __________________ is the result of mixing a solute in a solvent. A solution is a _____________________________. A suspension is ___________________. These will ________________ over time. The ______________________ effect determines if a mixture is a solution or a suspension. Light scatters through a suspension. Light does not scatter through a solution. Immiscible: Miscible: Units of concentration of a solution: 1] molarity 2] percent 3] parts per number (thousand, million, billion) 4] mole fraction 5] molality 6] normality For acids and bases: For oxidizing agents and reducing agents: 7] formality TTP 1] If the density of a 38% HCl solution is 1.19 g/mL, find its molarity, normality, mole fraction and molality 2] The density of a 99% acetic acid (vinegar) – HC2H3O2 is 1.05 g/mL, find M, N, m, χ. (molarity, normality, molality and mole fraction 3] Given a 1.25 M oxalic acid, H2C2O4, the density is 1.08 g/mL. Find percent solute by mass, molality, mole fraction and normality. Structural effects and solubility Recall oils are _______________ and water is _________________. Like dissolves _______. Polar solutes dissolve in water, but nonpolars dissolve in _________________ and ________. Soaps are : Hydrophobic: Hydrophilic: Vitamin A: Vitamin C: Pressure effects and solubility Henry’s Law: Equation: Temperature and solubility For gases: For ionic solids: (see graph p. 525) Saturated solutions: Unsaturated solutions: Supersaturated solutions: TTP: determine if the following solutions are saturated, supersaturated or unsaturated: 1] 4.0 g of NaCl at 100oC in 10.0 g of water 2] 12.0 g of KNO3 at 50 oC in 20 g of water 3] 14 g of NH4Cl at 40 oC in 25 g of water 4] 1.0 g of KCl at 30 oC in 5 g of water 5] 20 g of NaCl at 100 oC in 50 g of water 6] 0.14 g of Ce2(SO4)3 at 50 oC in 15 g of water Find the concentration of Ni+2 ions and Cl-1 ions in a solution prepared by diluting 20.0 mL of a 1.00 M NiCl2 solution to 1.00 L Vapor pressure of solutions For an ideal solution: Adding a non-volatile solute _________________ the vapor pressure of the ________________. For an ideal solution: (equation) Graph: Negative deviations occur when: Positive deviations occur when: For exothermic reactions, there is a __________________ interaction between the __________. For endothermic reactions, there is a ________________ interaction between the ___________. Ideal solutions obey: Binary liquid mixtures: These refer to a mixture where both components are _______________. The overall vapor pressure is the pressure of the first component + the pressure of the second component. You have to factor in the mole fraction of each component. For an ideal solution: Ptotal = PA + PB where Ptotal is the total pressure. PA is the pressure of the first component, and PB is the pressure of the second component. The pressure of PA = ΧAPpure liquid A ; PB = ΧBPpure liquid B TTP#1: What is the total vapor pressure at 25oC of a mixture of 3.00 mol of benzene, C6H6, and 2.00 mol of toluene, CH3C6H5. The vapor pressures of benzene and toluene at 25oC are 94.6 and 29.1 torr respectively. TTP#2: When 8.05 g of an unknown compound X was dissolved in 100.0 g of benzene, the vapor pressure of the benzene decreased from 100.0 torr to 94.8 torr at 26 oC. What is a] the mole fraction and b] the molar mass of X? Colligative properties of solutions (for nonelectrolytes): These refer to: For freezing point: The physical presence of the solute ______________ the freezing point of the solvent. This is because: Equation: kf values can be found on p. 537 For boiling point: A solute causes the boiling point of the solvent to _____________. This is because: Equation: TTP 1] If 25.0 g of glucose, C6H12O6, is dissolved in 200.0 g of water, what is the temperature the solution will freeze? 2] At what temperature will the solution in #1 boil? 3] The kf value for benzene, C6H6, is 5.12. Benzene freezes at 5.5 oC. If 10.0 g of carbon tetrachloride is placed in 50.0 g of benzene, at what temperature will the solution freeze? 4] Find the temperature that 1.00 g of benzaldehyde, C 6H5CHO, in 10.0 g of benzene will freeze. Finding the molar mass of compounds: 1] Find the molar mass of a compound that is a nonelectrolyte if 16.0 g of the compound when added to 180.0 g of water freezes at -1.38 oC. 2] Find the molar mass of a compound that is a nonelectrolytes if 5.00 g of the compound when dissolved in 25.0 g of water boils at 102.00 oC. Osmotic pressure Equation: 1] Find the molar mass of an unknown protein if 1.25 mg of the protein when added to water makes 1.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of the solution is 1.40 torr at 27.0 oC. For electrolytes: New equations: Where i = __________ ____factor. The van’t Hoff factor is the number of particles that form when an electrolyte is in water. For NaCl, i = For Fe(NO3)3 i = However, the predicted changes in boiling point, freezing point and osmotic pressure are generally less than those you would predict. This is because of __________________. Since opposite charges ________________, the separate ions get together and act as if they were a single particle, rather than separate particles. The _______________ concentrated a solution, the greater the deviation from predicted change. The _____________ the i value, the greater the deviation. Problems: 1] Find the molar mass of an electrolyte that is made up of an alkali metal and a -1 polyatomic anion if the solution freezes at -5.13 oC when 15.0 g of the compound is added to 220.0 g of water. 2] Find the minimum osmotic pressure needed to get fresh water out of seawater at 25.0 oC. The molarity of NaCl in seawater is 0.8214 M.