a Word Version of Nomenclature Flowchart
advertisement

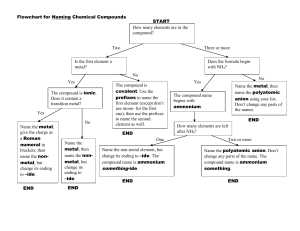
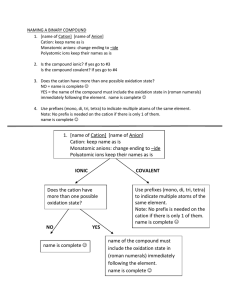
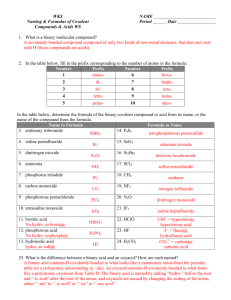
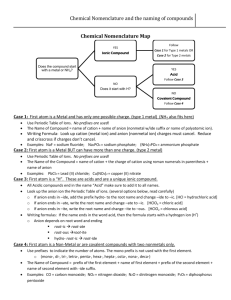
Nomenclature Flowchart 1. If the first element is a metal or NH4+, go to 2 or else go to 3. 2. The compound is a salt or a base. If the metal is a transition metal, go to A or else go to B. A. Determine the charge on the cation. Write name of the cation showing the charge as Roman numerals in parenthesis. Then write the name of the anion. Example - CrCl3 is chromium(III) chloride Au2SO4 is gold(I) sulfate B. Write the name of the cation. Then write the name of the anion. Example - ZnBr2 is zinc bromide Ca3(PO4)2 is calcium phosphate 3. If the first element is H, go to 4 or else go to 5. 4. The compound is an acid. If the formula contains O, go to A or else go to B. A. The compound is an oxyacid. If the polyatomic anion ends in -ate, go to 1 or else go to 2. 1. Name the polyatomic anion, replacing "ate" with "ic" and add the word acid. Example - H2CrO4 is chromic acid H2SO4 is sulfuric acid 2. Name the polyatomic anion, replacing "ite" with "ous" and add the word acid. Example - HIO2 is iodous acid H2SO3 is sulfurous acid B. Compound is a binary or (binary-like) acid. Write the prefix "hydro", the anion name with "ide" changed to "ic" and add the word acid. Example - HBr is hydrobromic acid H2S is hydrosulfuric acid HCN is hydrocyanic acid 5. The compound consists of 2 nonmetals. The compound is a covalent compound. Use prefixes (mono, di, tri, tetra, etc) to show the number of each element present in the compound. (The prefix mono is frequently left off the name of the first element.) Change the ending of the second element to "ide". Example - P2O5 is diphosphorous pentoxide SO3 is sulfur trioxide CO is carbon monoxide