Terms/Concepts to know:
advertisement

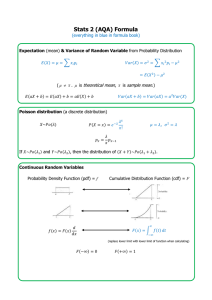
Hypothesis testing: Five steps for hypothesis testing: 1. 2. 3. 4. Samples M SD2 SD Populations Random selection: Convenience or haphazard selection: Random assignment: A first example: A doctor gives a patient a new type of anti-depressant. Is there any improvement compared to a larger population of depressed population? Assume that depression scores follow a "normal curve" (Population) M = 69.5 SD = 14.1 X = 41 1. Convert research questions to statistical hypotheses. 2. What are the characteristics of our comparison distribution? Why can we use the normal curve? Not all distributions are normal. 3. Determine "cut-off" scores. Conventional level of statistical significance One tailed vs. two tailed 4. Determine your observation or sample score. Convert observation to Z score. 5. Accept or reject the NULL hypothesis. How would we write it down? A second example: Is memory affected by stress? Ask 25 people to give a talk and then remember a set of photographs. Mean recall = 48, SD=7, General population mean=53 Shift to a sample of observations from a single observation. 3 key characteristics of a distribution of means. 1. 2. 3. So how do we correct the problem? Formulas: