Bio 504 Name : Review : Unicellular Organisms Part 1
advertisement

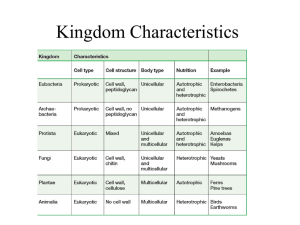
Bio 504 Name : Review : Unicellular Organisms Part 1- Prokaryote vs Eukaryote 1. How do prokaryotes and eukaryotes differ in terms of: size, DNA, reproduction, # cells, and organelles. Prepare a table that contains this information. 2. Why are viruses not considered alive? 3. What is a capsid? 4. How are viruses classified? 5. Draw and label the lytic cycle of a virus. 6. Describe the lysogenic cycle of replication in a virus. 7. What is a prion? How can they cause diseases? 8. Briefly describe 3 ways viruses are used in biotechnology. Part 2- Bacteria vs Archaea 1. What are the 3 most common shapes of bacteria and archaea. What name is associated with each of these shapes? 2. How do autotrophic bacteria make their food? 3. How do autotrophic archaea make their food? 4. What are mesophiles? Give an example. 5. What are extremophiles? Give an example. 6. How do binary fission and conjugation differ? 7. What is an endospore? 8. Differentiate between a Gram positive and a Gram negative strain of bacteria. 9. Name 3 ways bacteria and/or archaea are detrimental to our health. 10. Name 3 ways bacteria and/or archaea are useful to us. Part 3- Protists 1. Name 3 ways protists differ from bacteria and archaea? How are they similar? 2. Name the 3 categories of protists. 3. What are the 2 roles of pseudopods? Name a protist that has these structures. 4. What are the 2 roles of cilia? Name a protist that has these structures. 5. What is the role of a flagellum? 6. Name 2 characteristics of sporozoa. 7. How are slime moulds and water moulds like fungi? Why are they not considered fungi? 8. What is phytoplankton? 9. What is particular about the cell walls of diatoms? 10. What is special about the flagella in dinoflagellates? 11. What is a red tide? 12. What is bioluminescence? 13. Why is it difficult to categorise the euglena? 14. Name 3 types of seaweed. 15. Explain why seaweed is considered a protist and not a plant even though it is multicellular. 16. What is a holdfast?