archaeabacteria video

ARCHAEABACTERIA VIDEO
Watch the video and answer the questions below goo.gl/74vG6L
1.
Where can archaea be found? Where were they first found?
2.
How does the cell wall of archaea differ from the common cell wall of bacteria?
3.
How do the different phospholipids used by archaea allow them to withstand harsh environments?
4.
If you wanted to find a photosynthetic archaea where would be a good place to look? Why?
5.
Where do halophiles live?
6.
Why are some archaea classified as thermophiles?
7.
What is an example of a mutualistic relationship between archaea and another organism?
CAVING FOR CURES---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Watch the video and answer the questions below. goo.gl/ZYYgpk
1.
Explain why caves are a unique environment to look for living organisms used to make drugs.
2.
Why do scientists feel that environments which encourage microbial competition are good places to look for drugs?
3.
What sorts of clues do researchers look for to identify potential microbial colonies in caves?
4.
What two factors determine the biological activity of a compound? How does this help explain how some drugs can mimic natural compounds?
5.
What is one basic advantage natural compounds have over wholly synthetic compounds in the search for new drugs?
BOOK RESEARCH
Preview section 23.1, “Prokaryotes”.
1.
Please read page 461. a) Arcahea and Bacteria are both (prokaryotes/eukaryotes) b) Arcahea and Bacteria are both (unicellular/multicellular) c) Arcahea and Bacteria are (autotrophic/heterotrophic/either)
ARCHAEA
2.
Look at figure 23-1 on page 461. a.
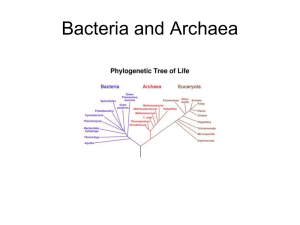
According to rRNA analysis, eukaryotes are more closely related to (bacteria/archaea).
3.
Please read the first paragraph under the section, “Domain Archaea” on page 462. a.
Describe two reasons why archaea are not classified as bacteria. i.
ii.
b.
Where were archaea first found?
4.
Please read paragraphs under the section, “Archaeal Groups” on page 462. a.
Name and describe the three groups of archaea. i.
ii.
iii.
BACTERIA
5.
Please read page 463. Describe two ways bacteria are classified. a.
b.
6.
Table 25-1 summarizes the characteristics of several protest phyla. a) Protists are (unicellular/multicellular/both). b) Protists are (heterotrophic/autotrophic/both). c) Protists are (able to/not able to) move at some time in their life cycles.