MatterVocab
advertisement

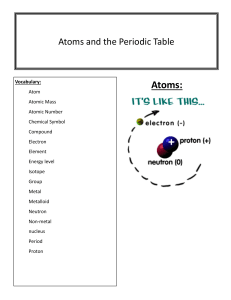
Matter Vocabulary Matter: anything that has mass and takes up space. All matter has mass and volume. Mass: measure of the amount of matter in an object. Constant. Volume: amount of space an object takes up. Weight: measure of the gravitational force on an object. Changes. Density: ratio of the mass of a substance to the volume of the substance. D=M V States of matter: physical states in which a substance can exist. Solid Liquid Gas Shape + - Volume + + - Change of state: change of a substance from one physical state to another This change uses or loses energy Melting: change of state from solid to liquid. Energy added. Freezing: change of state from liquid to solid. Energy removed. Evaporation: change of a substance from liquid to gas at the surface. Boiling: change of a liquid to a gas throughout the substance. Condensation: change of a gas to a liquid. Sublimation: change of a solid to a gas Physical properties: characteristics that can be observed without changing the substance. Do not change when the amount of the substance changes. Examples: Density, color, hardness, thermal conductivity Ductility: able to be pulled into a wire Malleability: able to be made into flat sheets Chemical properties: characteristics that describe a substance’s composition. Physical change: change of matter from one substance to another. The chemical properties of matter do not change. Chemical change: substance changes into entirely new substance. The new substance has different properties than the original. Atom: smallest indivisible particle of matter Molecule: 2 or more atoms bonded together Element: a substance that cannot be broken down Compound: combination of different elements Proton: positive charge. In nucleus. Has mass. Neutron: no charge. In nucleus. Has mass. Electron: negative charge. In cloud. Has no mass. Atomic Number: number of protons Atomic Mass: number of protons plus neutrons Ion: an atom that has lost or gained an electron—has a charge Isotope: atoms of the same element with different number of neutrons