Flash cards matter
advertisement

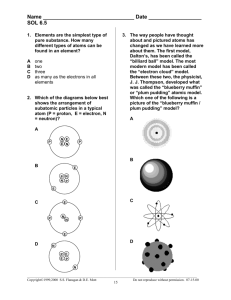
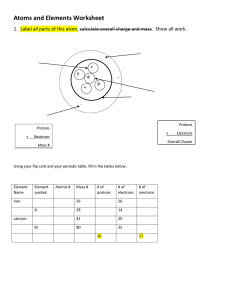
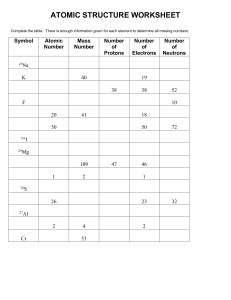
matter anything that takes up space and has mass atoms smallest particle of matter electron negative charge surrounds the nucleus proton positive charge - in the nucleus neutron no charge - in the nucleus atomic number equal to the number of protons (also electrons) atomic mass equal to protons + neutrons (the nucleus) neutral atom # of protons and electrons are equal (no charge) element pure substance consisting of one atom isotope atoms of the same element with different # of neutrons chemical compound substance of two or more elements in definite proportions chemical formula shows what elements and how many are in a compound (H2O) chemical bonds hold elements together coalent bond sharing of electrons ionic bond transferring of electrons ion a charged atom (gain or lost an electron) positive charged ion has lost an electron negatively charged ion has gained an electron