Chapter 3 Learning Targets
advertisement

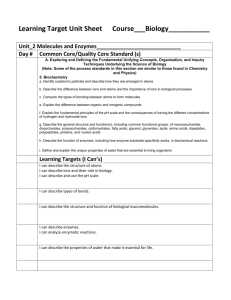
I know this stuff! I could use some help... Ahh! What is this? Chapter 3 Learning Targets Write out the answers to the questions and assignments of these learning targets on a separate sheet of paper! DUE THE DAY OF THE TEST!!!! The goal of this unit is to be able to say “I can…” How do you feel? Date(s) Discussed “I can…” _____________ _____________ 1. identify the 4 major organic compounds important to living organisms Question: What are the 4 major organic compounds important to living organisms? _____________ _____________ 2. identify and characterize the elements that make up the major organic molecules and describe what they are used for Question: What elements make up the major organic molecules? What are their characteristics, and what they are used for? _____________ _____________ 3. describe the importance of carbon in forming organic molecules Question: What is the importance of carbon in forming organic molecules? _____________ 4. define monomers and polymers and provide examples of each Question: What are monomers and polymers? Give 2 examples of each. _____________ _____________ _____________ 5. define and draw out the processes of dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis Assignment: Define and draw out the processes of dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis with an example of an organic compound. _____________ _____________ 6. Explain what the names of the monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides stand for. Explain why carbohydrates are important? Question: What do the names of the monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides stand for? Why are carbohydrates important? _____________ _____________ 7. identify and draw the 3 monosaccharides, 3 disaccharides, and a polysaccharide Assignment: List and draw the 3 monosaccharides, the 3 disaccharides (which monosaccharides they are made up of), and a polysaccharide _____________ _____________ 8. describe the Benedict’s test and what it tests for Assignment: Describe, in detail, the Benedict’s test (include what it tests for). _____________ _____________ 9. describe the iodine test and what it tests for Assignment: Describe, in detail, the iodine test (include what it tests for). _____________ _____________ 10. define the term “isomer” Question: What is an isomer? ____________ _____________ _____________ _____________ 11. Identify the building blocks of proteins and provide an example. Explain why proteins are important. Questions: What are the building blocks of proteins (give an example)? Why are proteins important? 12. define a peptide bond, identify where a peptide bond is found, and compare and contrast dipeptides and polypeptides Question: What is a peptide bond, and where it is found? What are dipeptides and polypeptides? _____________ _____________ 13. describe the Xanthoproteic (nitric acid) test and what it tests for Assignment: Describe, in detail, the Xanthoproteic test (include what it tests for). _____________ _____________ 14.explain the characteristics of enzymes Assignment: List and describe, in detail, the characteristics of enzymes. _____________ _____________ 15. define an enzyme, substrate, and enzyme-substrate complex and be able to recognize them Assignment: Define an enzyme, substrate, and enzyme-substrate complex and draw a picture of them. _____________ _____________ 16. explain the lock and key hypothesis of enzyme function Question: What is the lock and key hypothesis of enzyme function? _____________ _____________ 17. describe how catalysts affect the rate of reactions and identify what else can function as catalysts Question: How does a catalyst affect the rate of a reaction, and what else can function as a catalyst? _____________ _____________ 18. define what coenzymes are, describe how they help enzymes, and recognize where coenzymes can be obtained Question: What are coenzymes? How do coenzymes function to help enzymes? Where can you obtain coenzymes? _____________ _____________ 19. define the term “inhibitors” Question: What are inhibitors? _____________ _____________ 20. describe the types of inhibitors Question: What are the types of inhibitors? _____________ _____________ 21. identify the building blocks of lipids and explain how lipids form. Distinguish the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids and provide examples. Explain why lipids are important. Question: What are the building blocks of lipids and how do lipids form? What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids? Give examples of lipids. Why are lipids important? _____________ _____________ 22. describe the brown paper, Sudan IV, and lighter fluid (solubility) tests and what they test for Assignment: Describe, in detail, the brown paper, Sudan IV, and lighter fluid(solubility) tests (include what they test for). _____________ _____________ 23. Identify and draw the building block of nucleic acids and the parts of the monomer. Identify the 2 examples of nucleic acids. Questions: What are the building blocks of nucleic acids? _____________ _____________ 24. recognize various organic molecules/building blocks from the flash cards and identify what types of organic molecules contain the various functional groups Assignment: Create flash cards of the structures of monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides, amino acids, proteins, fatty acids, glycerol, lipids, and nucleic acids in order to get credit for this learning target *Know the flash cards forwards and backwards and know what types of organic molecules contain the various functional groups. Be able to recognize various organic molecules or the building blocks of them from the flash cards.*