Macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids
advertisement

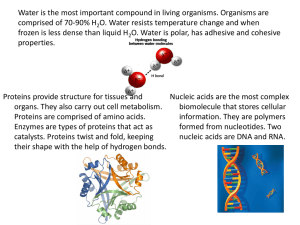
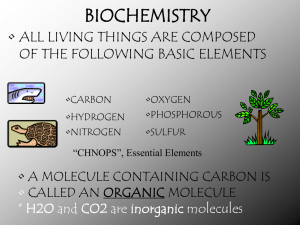
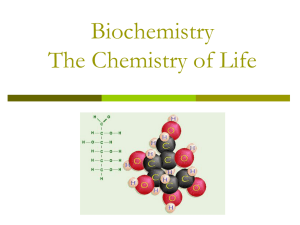
Macromolecules Standard: 1.h Students know most macromolecules in cells and organisms are synthesized from a small collection of simple precursors. Objective: Students will be able to distinguish between four types of macromolecules found in all organisms. Duration: 45 minutes Instruction: Teacher can post information on overhead or board for students to copy down in their notes or on to macromolecule graphic organizer. There are four groups of substances make up most living things. All of these macromolecules (large molecules) are organic (they contain carbon). Carbohydrates – a group of molecules that include sugars, starches and cellulose. They store energy and provide shape to organisms. Carbohydrates are made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. The basic chemical formula is CH2O. Monosaccharides (one sugar) provide quick energy because they are easily broken down by the body. Monosaccharides and disaccharides link together to form polysaccharides (many sugars) ; such as starch that stores energy in plants, or glycogen that stores energy in animals. Glucose (C6H12O6 ), one of the most common sugars, is the product of photosynthesis. Cellulose is one of the most abundant compounds found in nature. It is what gives support to plant cells, giving celery its crunch! Lipids – Molecules that include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids and steroids. Lipids are made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. The basic unit is made of glycerol and three long chains of fatty acids. Lipids are not soluble in water (they do not dissolve). Fats provide long term energy storage in animals, as well as insulation. Phospholipids form the cell membrane that surrounds all cells. Steroids such as cholesterol provide structure and control functions. Proteins – Large complex molecules made up of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sometimes sulfur. The basic unit is the amino acid. There are 20 different amino acids that combine in different combinations to make up over 100,000 different proteins. Proteins function in movement (muscles), structure, transport of materials across the cell and defense (antibodies). Enzymes are special proteins that help control chemical reactions in the cell. Nucleic Acids – Large complex molecules made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorus. The basic unit is the nucleotide. Nucleotides contain a phosphate group, sugar and one of 5 nitrogenous bases. There are two basic types of nucleic acids, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). DNA carries the genetic information – your body’s blueprint. RNA makes the proteins. Most nucleic acids are found in the nucleus of the cell.