Quantum-Wave Mechanical Theory
advertisement

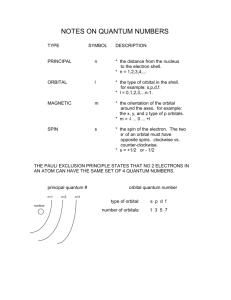
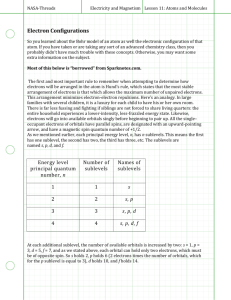
TEST: overview Topics covered: Electrons - Bohr Model & Atomic Emission Spectra - Quantum-Wave Mechanical Theory - 4 Quantum Numbers - Ground State Electron Configuration - Aufbau Principle - Noble Gas Notation - Orbital Diagram - S,P,D,F – Blocks (periodic table) The Quantum-Wave Mechanical Model (Theory) - It determines the allowed energies (quantum) an electron can have & How likely it is to find the electron orbiting the nucleus. Also, electrons move around the nucleus in a wave pattern, having a specific frequency & wavelength (which determines the energy of an electron). looks something like a composite of quarks surrounded by clouds of uncertainty The Quantum-Wave Mechanical Model (Theory) • This model does not have orbitals, rather regions of probability. • Atomic orbitals are regions of space in which there is a high probability (90%) of finding an electron. Except the s orbital (only 10%). ** The theory states that any electron in an atom can be completely described(located) by 4 Quantum Numbers. 4 Quantum #’s – (describe the electrons location) 1. Principle Quantum Level 2. Sub-levels 3. Orbital’s 4. Spin of Electrons ( …..How electrons fill in each orbital) 1. Principal Quantum Numbers also called “Energy Levels” - symbol “n” - “n” are always integers 1 ,2 ,3 ,4…7 - And are related to Periods on the Periodic Table see below. 2. electron Sub-levels . S ~ sublevel………..holds a total of 2 e- P ~ sub-level.……….holds a total of 6 e- d ~sub-level…………holds a total of 10 e- f ~ sub-level………. holds a total of 14 e- ________________________________________________________ Below – a atomic model with Energy Levels, 2e- Sublevels, & the maximum amount of 2e- 6e- electrons they can hold. 2e- 6e- 10e- Quantum Numbers #1 = Energy Levels + 1&2 #2 = Sublevels 1st energy level has one sublevel 2nd (sublevel breakdown, below) 1s energy level has two sublevels 2s , 2p 3rd energy level has three sublevels 3s , 3p , 3d 4th energy level has four sublevels 4s , 4p , 4d , 4f 5th energy level has four sublevels 5s , 5p , 5d , 5f 6th energy level has four sublevels 6s , 6p , 6d , 6f 7th energy level has four sublevels 7s , 7p , 7d , 7f • 3rd Quantum Number • All orbital’s hold 2 electrons only . deals with electron Orbital’s. (no exceptions). S~ has 1 orbital .……holds a total of 2 e- P ~ has 3 orbitals ……holds a total of 6 e- d ~ has 5 orbitals ……holds a total of 10 e- f ~ has 7 orbitals ……holds a total of 14 e- • All orbital’s in any one sublevel (of the same element) are For example, of equal energy all three, 2p orbital’s for all elements are of equal energy. • the energy sublevels within an energy level have different energies. for the same energy level…. low Energy s p d f high Energy For example, the 2p orbitals are of higher energy than the 2s orbital. Quantum Sublevels are labeled S, P, D, F S – orbital’s (has a Spherical shape) P - orbital’s (has a figure 8 shape) or “dumbbell” D - orbital’s (has a Clover leaf shape) 4th Quantum Number, deals with electrons filling orbital’s. Each box (below) represents one orbital - Pauli Exclusion Principle = States that a maximum of two electrons may occupy a single atomic orbital, but only if the electrons have opposite spins. Sublevels and orbitals S sub-level has 1 orbital …. P sub-level has 3 orbital’s ………….. D sub-level has 5 orbital’s ………………………… F sub-level has 7 orbital’s - Hund’s Rule = States that single electrons with the same spin must occupy each equalenergy orbital before additional electrons with opposite spins can occupy the same orbital’s. P sub-level how do all 6 electrons fill in?