Vocabulary Terms for Earth Science Midterm
advertisement
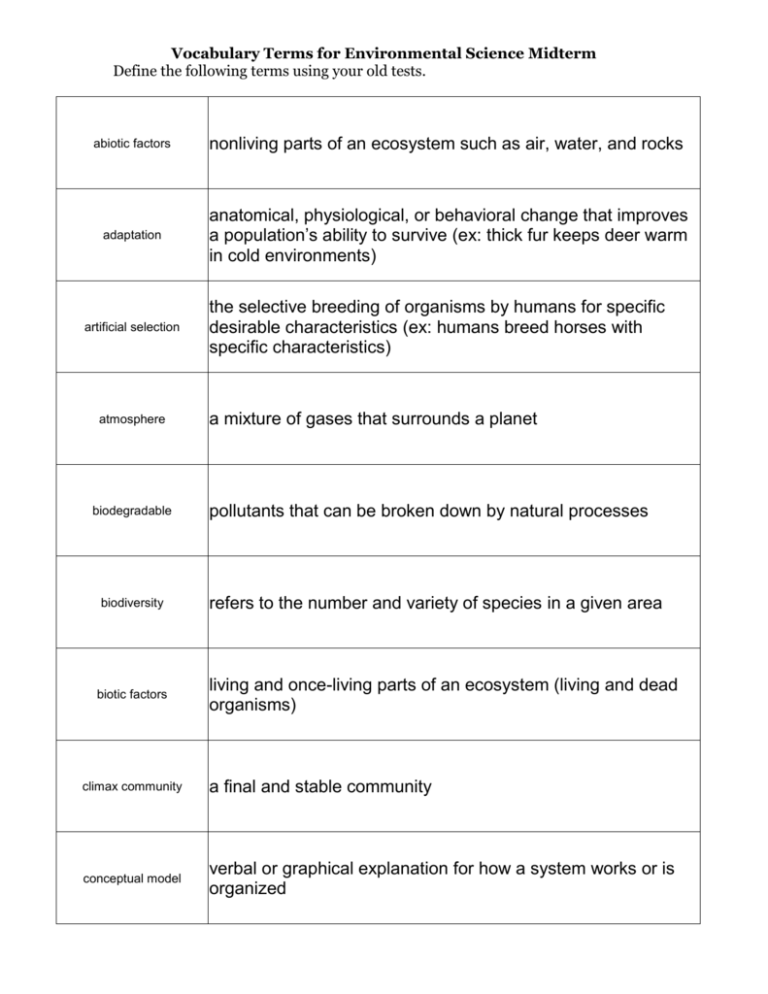
Vocabulary Terms for Environmental Science Midterm Define the following terms using your old tests. abiotic factors nonliving parts of an ecosystem such as air, water, and rocks adaptation anatomical, physiological, or behavioral change that improves a population’s ability to survive (ex: thick fur keeps deer warm in cold environments) artificial selection atmosphere biodegradable biodiversity biotic factors the selective breeding of organisms by humans for specific desirable characteristics (ex: humans breed horses with specific characteristics) a mixture of gases that surrounds a planet pollutants that can be broken down by natural processes refers to the number and variety of species in a given area living and once-living parts of an ecosystem (living and dead organisms) climax community a final and stable community conceptual model verbal or graphical explanation for how a system works or is organized core correlation data earthquake Earth’s innermost compositional layer association used to study a subject when using an experiment is impossible or unethical information gathered during an experiment vibration caused by slippage along a fault ecological footprint the productive area of Earth needed to support the lifestyle of one person in a particular country ecological succession a gradual process of change and replacement of the types of species in a community ecology Environmental science experiment study of how living things interact with each other and their nonliving environment study of how humans interact with science procedure for testing a hypothesis under controlled conditions food chain a linear sequence in which energy is transmitted from one organism to the next as each organism eats another organism food web the many feeding relationships that are possible in an ecosystem geosphere the mostly solid, rocky part of the Earth; extends from the center of the core to the surface of the crust graphical model maps and charts that illustrated data such as positions or amounts graphically (ex: positions of stars) hydrosphere hypothesis all the water on or near the Earth’s surface, including oceans, polar ice caps, rock layers beneath Earth’s surface, and clouds testable explanation for an observation old-field succession a type of succession that occurs on abandoned farmland observation information gathered by using the senses (sight, hearing, smell, and touch) nonrenewable resources resources that are consumed at a faster rate than produced physical model pollution recharge zone three-dimensional representation you can touch that closely resemble the object or systems they represent changed in air, water, and soil that adversely affects the environment land surface area where water enters an aquifer renewable resources resources that can theoretically last forever and are constantly being formed in a short period of time secondary succession a common type of succession that occurs on a surface where an ecosystem has previously existed sustainability the condition in which human needs are met in such a way that a human population can survive indefinitely thermocline boundary between warm and cold water in an ocean or lake thermosphere values the topmost layer of Earth’s atmosphere principles or standards we consider important