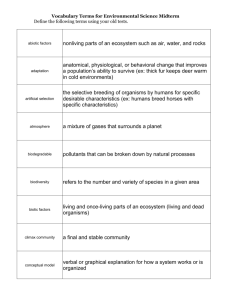
MIDTERM REVIEW GUIDE-ENVIRONMENTAL BIOLOGY 2011

MIDTERM REVIEW GUIDE-ENVIRONMENTAL BIOLOGY 2011-12
Study Tips:
1.
Review all class notes
2.
Review activity worksheets
3.
Review unit tests
4.
Review all labs and handouts (including diagrams, pictures, and animations on computer)
5.
Study review games (Jeopardy)
START STUDYING IN ADVANCE, A LITTLE AT A TIME, AND DO NOT WAIT TO THE
LAST MINUTE. STUDY HARD BUT STRESS SOFTLY. GOOD LUCK.
TOPICS:
NATURE OF SCIENCE
1. What is in the realm of science? (What will science try to explain and not try to explain)
2. In order to be testable in science it must be ___________ & _________________
3. Steps of the scientific method
4. Controlled experiment-control group and experimental group, control variables
(constant) and independent and dependent variables.
5. Difference between inference & observation
6. Difference between quantitative & qualitative observations
7. Define a theory in science
GRAPHING
1.
How to draw a graph of data
2.
Where does the independent and dependent variable appear on a graph?
3.
Interpreting graphs or finding the pattern (like broom game or knives & forks).
ECOSYSTEM ECOLOGY
1.
Know the following terms: a.
Food chain b.
Food web c.
Trophic levels d.
Primary producer e.
Autotroph and heterotroph f.
Primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary consumers g.
Decomposers h.
Herbivore, omnivore, carnivore, and detrivore
1
i.
Biotic and abiotic
2.
How much energy is available to the next trophic level (be able to calculate)?
3.
What happens to the energy not passed to next trophic level?
4.
What is different about how energy and nutrients pass or move through an ecosystem or food chain?
5.
Define ecosystem
6.
Where does the original source of energy for living things come from?
7.
Know the three types of pyramids and what information can be obtained by looking at pyramids?
8.
What happens to the amount of energy, biomass, and usually numbers as you move up a pyramid?
9.
Basics of water cycle (evaporation, precipitation, condensation, and transpiration)
10.
Carbon cycle a.
Processes that move carbon from one carbon to another (photosynthesis, cell respiration, burning of fossil fuels, and decomposition of dead plants and animals) Which pool does each process take carbon from and what pool does it move carbon to and in what form (inorganic carbon dioxide or organic form) b.
Define global warming and what is responsible for it. How can we help improve global warming? c.
How do plants and animals affect the movement of carbon?
11.
Direction energy flows through a food chain
12.
Reactants and products of cell respiration and photosynthesis and what organisms perform these two processes? Where are the reactants obtained?
13.
What organism has damaged the web of life the most?
14.
What is the purpose of photosynthesis and cell respiration?
15.
What happens if an organism in a food web goes extinct?
16.
What are the two major processes that Ecosystem ecologists study?
COMMUNITY ECOLOGY
1.
Define community
2.
What is the major focus of study for community ecologists?
3.
Define predator, prey, predation
4.
What is the importance of predation?
5.
Define co-evolution
6.
What happens to predators and prey when one increases or decreases/
7.
Three types of symbiosis
8.
Competitive exclusion principle
9.
Habitat vs. niche
10.
Resource partitioning
11.
Succession a.
Primary vs. secondary succession b.
Pioneer species or organism (lichen)
2
c.
Climax community d.
Stages in succession e.
Define succession
POPULATION ECOLOGY
1.
What is linear growth and how is it represented on a graph?
2.
What is exponential growth and how is it represented on a graph?
3.
What is an S-shaped curved graph?
4.
What is carrying capacity?
5.
What are limiting factors? a.
Density independent factors b.
Density dependent factors
6.
Define a population
7.
What type of growth is human population in?
8.
What are problems with human population growth?
9.
What happens if birthrate is greater than death rate?
3