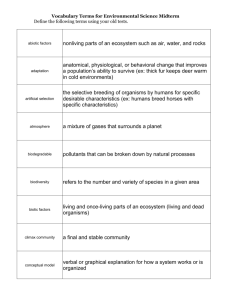
Ecosystem and Biome Vocabulary
advertisement
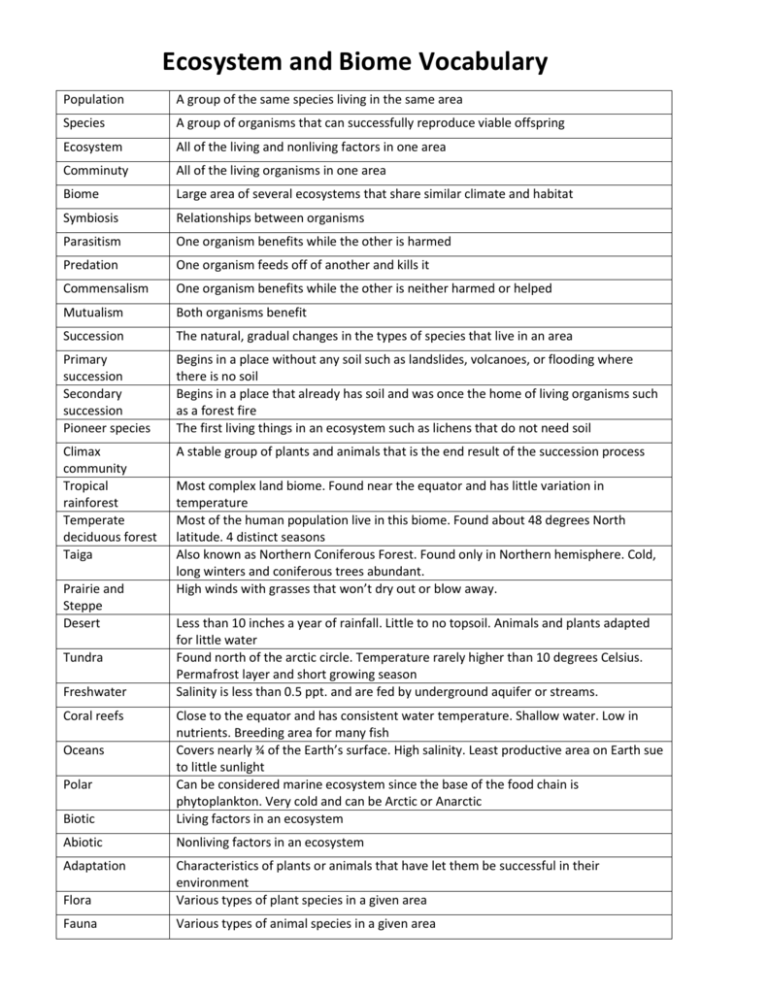
Ecosystem and Biome Vocabulary Population A group of the same species living in the same area Species A group of organisms that can successfully reproduce viable offspring Ecosystem All of the living and nonliving factors in one area Comminuty All of the living organisms in one area Biome Large area of several ecosystems that share similar climate and habitat Symbiosis Relationships between organisms Parasitism One organism benefits while the other is harmed Predation One organism feeds off of another and kills it Commensalism One organism benefits while the other is neither harmed or helped Mutualism Both organisms benefit Succession The natural, gradual changes in the types of species that live in an area Primary succession Secondary succession Pioneer species Begins in a place without any soil such as landslides, volcanoes, or flooding where there is no soil Begins in a place that already has soil and was once the home of living organisms such as a forest fire The first living things in an ecosystem such as lichens that do not need soil Climax community Tropical rainforest Temperate deciduous forest Taiga A stable group of plants and animals that is the end result of the succession process Prairie and Steppe Desert Tundra Freshwater Coral reefs Most complex land biome. Found near the equator and has little variation in temperature Most of the human population live in this biome. Found about 48 degrees North latitude. 4 distinct seasons Also known as Northern Coniferous Forest. Found only in Northern hemisphere. Cold, long winters and coniferous trees abundant. High winds with grasses that won’t dry out or blow away. Less than 10 inches a year of rainfall. Little to no topsoil. Animals and plants adapted for little water Found north of the arctic circle. Temperature rarely higher than 10 degrees Celsius. Permafrost layer and short growing season Salinity is less than 0.5 ppt. and are fed by underground aquifer or streams. Biotic Close to the equator and has consistent water temperature. Shallow water. Low in nutrients. Breeding area for many fish Covers nearly ¾ of the Earth’s surface. High salinity. Least productive area on Earth sue to little sunlight Can be considered marine ecosystem since the base of the food chain is phytoplankton. Very cold and can be Arctic or Anarctic Living factors in an ecosystem Abiotic Nonliving factors in an ecosystem Adaptation Flora Characteristics of plants or animals that have let them be successful in their environment Various types of plant species in a given area Fauna Various types of animal species in a given area Oceans Polar