Joints WS Name__________________________Per____ A. Match
advertisement
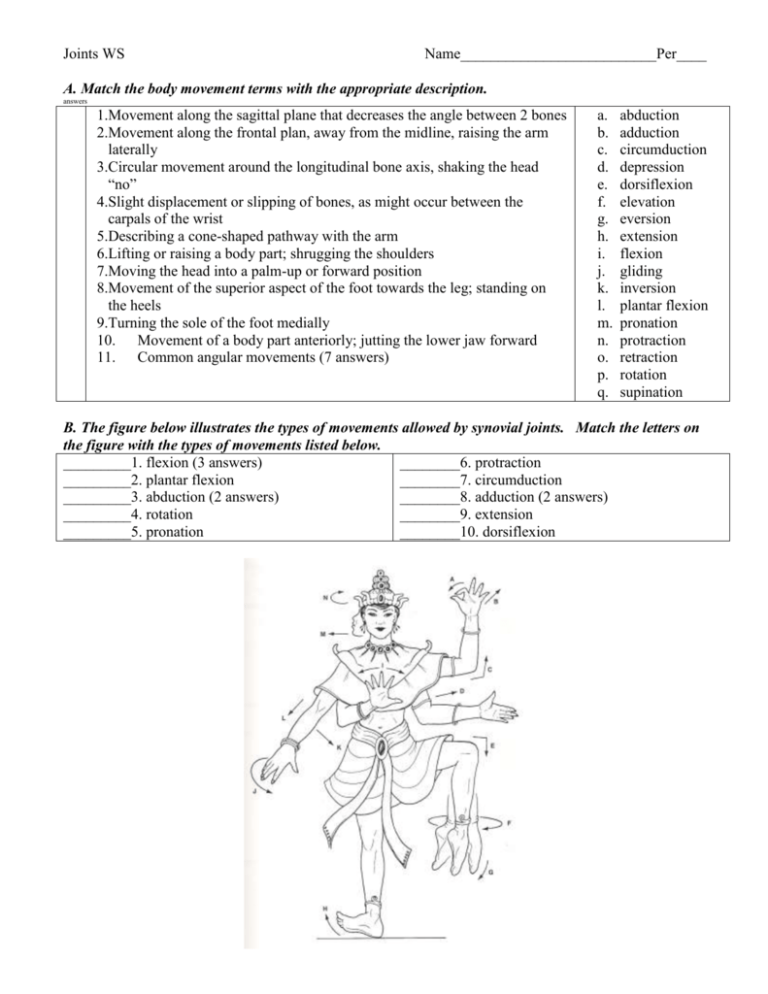
Joints WS Name__________________________Per____ A. Match the body movement terms with the appropriate description. answers 1.Movement along the sagittal plane that decreases the angle between 2 bones 2.Movement along the frontal plan, away from the midline, raising the arm laterally 3.Circular movement around the longitudinal bone axis, shaking the head “no” 4.Slight displacement or slipping of bones, as might occur between the carpals of the wrist 5.Describing a cone-shaped pathway with the arm 6.Lifting or raising a body part; shrugging the shoulders 7.Moving the head into a palm-up or forward position 8.Movement of the superior aspect of the foot towards the leg; standing on the heels 9.Turning the sole of the foot medially 10. Movement of a body part anteriorly; jutting the lower jaw forward 11. Common angular movements (7 answers) a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. m. n. o. p. q. abduction adduction circumduction depression dorsiflexion elevation eversion extension flexion gliding inversion plantar flexion pronation protraction retraction rotation supination B. The figure below illustrates the types of movements allowed by synovial joints. Match the letters on the figure with the types of movements listed below. _________1. flexion (3 answers) ________6. protraction _________2. plantar flexion ________7. circumduction _________3. abduction (2 answers) ________8. adduction (2 answers) _________4. rotation ________9. extension _________5. pronation ________10. dorsiflexion C. Match the name of the joint type with their description. answers 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. typically allows a slight degree of movement includes joints between vertebral bodies and pubic symphysis essentially immovable joints sutures are the most remembered examples characterized by cartilage connecting the bony portions all characterized by a fibrous articular capsule lined with a synovial membrane surrounded by a joint cavity 7. all are freely movable or diarthrotic 8. bone regions are united by fibrous connective tissue 9. include the hip, knee, and elbow joints a. cartilaginous b. fibrous c. synovial D. Describe the structure and function of the following parts of a synovial joint. Then, draw leader lines and label the diagram with the parts listed. Articular cartilage Synovial membrane Joint cavity Fibrous capsule E. Answer the following questions. 1. What is a ligament? 2. What is a tendon? 3. What is a bursa and what is bursitis? 4. Describe the movement of the origin and insertion bones during muscle contraction. F. Match the joint subcategories with their description. Then, place an asterisk (*) next to all choices that are examples of synovial joints. answers 1. joint between skull bones 2. joint between axis and atlas 3. hip joint 4. intervertebral joints 5. joint between forearm bones and wrist 6. elbow 7. interphalangeal joints 8. intercarpal joints 9. joint between skull and vertebral column 10. joint between jaw and skull 11. joints between proximal phalanges and metacarpals 12. a multiaxial joint a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. ball and socket condyloid gliding hinge pivot saddle suture symphysis synchondrosis syndesmosis