ARTICULATIONS (JOINTS)
advertisement

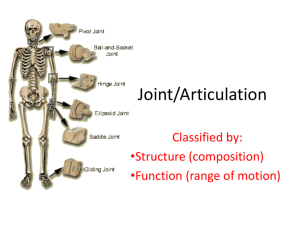
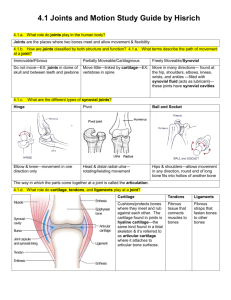
OBJECTIVES ARTICULATIONS (JOINTS) SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. 2. 3. 4. Identify the purpose of joints. Differentiate between the functional and structural classification of joints Identify the 4 parts of a synovial joint Identify the 6 types of synovial joints and their movement CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS PURPOSE Hold bones together Provide mobility A. FUNCTIONAL SYNARTHROSES – Do not move (sutures of skull) AMPHIARTHROSES – Slightly movable (vertebrae) DIARTHROSES – Freely movable (knee, elbow) CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS B. STRUCTURALLY FIBROUS – BONES UNITED BY FIBROUS TISSUE – SUTURES OF SKULL 1 CARTILAGINOUS – Bones connected by cartilage - Can be slightly movable as in symphysis pubis - Can be movable as in ephiphyseal plates of long bones or ribs to sternum SYNOVIAL - Ends of bones are separated by a cavity filled with synovial fluid 4 parts of a synovial joint 1. ARTICULAR CARTILAGE – hyaline cartilage covering ends of bones 2. FIBROUS ARTICULAR CAPSULE – fibrous connective tissue covering the joint 3. Joint cavity that contains lubricating fluid 4. Reinforcing ligaments surrounding joint 2 TYPES OF SYNOVIAL JOINTS PLANE (GLIDING) JOINT 1. PLANE JOINT – HORIZONTAL MOVEMENTS BETWEEN FLAT OR SLIGHTLY CURVED BONES - CARPALS & TARSALS 2. HINGE JOINT – MOVEMENT BACK & FORTH IN ONE PLANEKNEE & ELBOW HINGE JOINT 3. PIVOT JOINT – ROTARY MOVEMENT ON A CENTRAL AXIS - ATLAS & AXIS - ULNA & RADIUS 4. CONDYLOID JOINT – OVAL END OF ONE BONE FITS INTO OVAL CUP OF ANOTHER -BETWEEN METACARPALS & PHALANGES (KNUCKLES) PIVOT JOINT CONDYLOID JOINT 3 5. SADDLE JOINT – 2 SADDLE SHAPED JOINTS THAT MOVE 90 DEGREES OVER ONE ANOTHER SADDLE JOINT - BETWEEN METACARPAL & CARPAL OF THUMB 6. BALL & SOCKET – MOVEMENT IN MANY PLANES ; ROTATION - HIP - SHOULDER BALL & SOCKET JOINT 4