JOINTS
advertisement
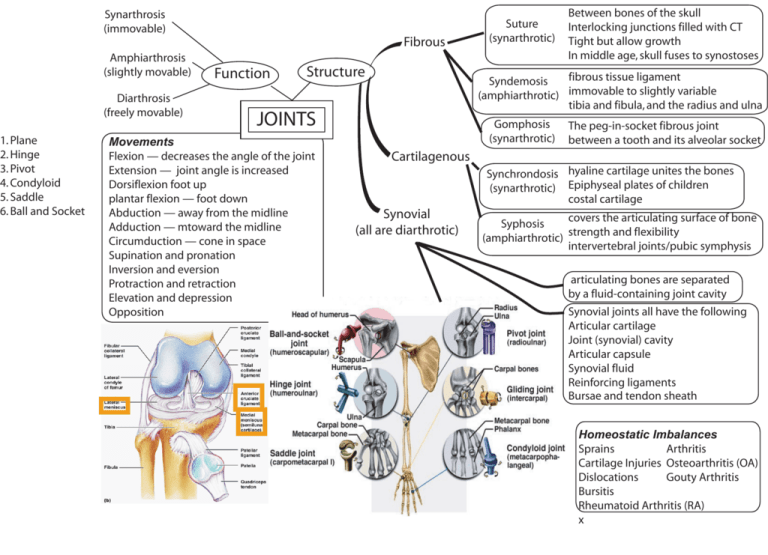
1. Plane 2. Hinge 3. Pivot 4. Condyloid 5. Saddle 6. Ball and Socket Synarthrosis (immovable) Amphiarthrosis (slightly movable) Diarthrosis (freely movable) Fibrous Function Structure fibrous tissue ligament Syndemosis (amphiarthrotic) immovable to slightly variable tibia and fibula, and the radius and ulna JOINTS Movements Flexion — decreases the angle of the joint Extension — joint angle is increased Dorsiflexion foot up plantar flexion — foot down Abduction — away from the midline Adduction — mtoward the midline Circumduction — cone in space Supination and pronation Inversion and eversion Protraction and retraction Elevation and depression Opposition Suture (synarthrotic) Between bones of the skull Interlocking junctions filled with CT Tight but allow growth In middle age, skull fuses to synostoses Gomphosis (synarthrotic) The peg-in-socket fibrous joint between a tooth and its alveolar socket Cartilagenous Synchrondosis hyaline cartilage unites the bones (synarthrotic) Epiphyseal plates of children costal cartilage Synovial (all are diarthrotic) covers the articulating surface of bone Syphosis strength and flexibility (amphiarthrotic) intervertebral joints/pubic symphysis articulating bones are separated by a fluid-containing joint cavity Synovial joints all have the following Articular cartilage Joint (synovial) cavity Articular capsule Synovial fluid Reinforcing ligaments Bursae and tendon sheath Homeostatic Imbalances Arthritis Sprains Cartilage Injuries Osteoarthritis (OA) Dislocations Gouty Arthritis Bursitis Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) x











