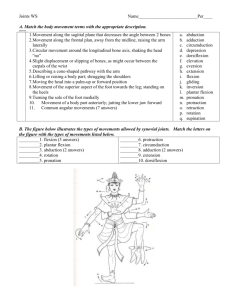
WORKSHEET5 INTRO TO JOINTS! What are the major types of
advertisement
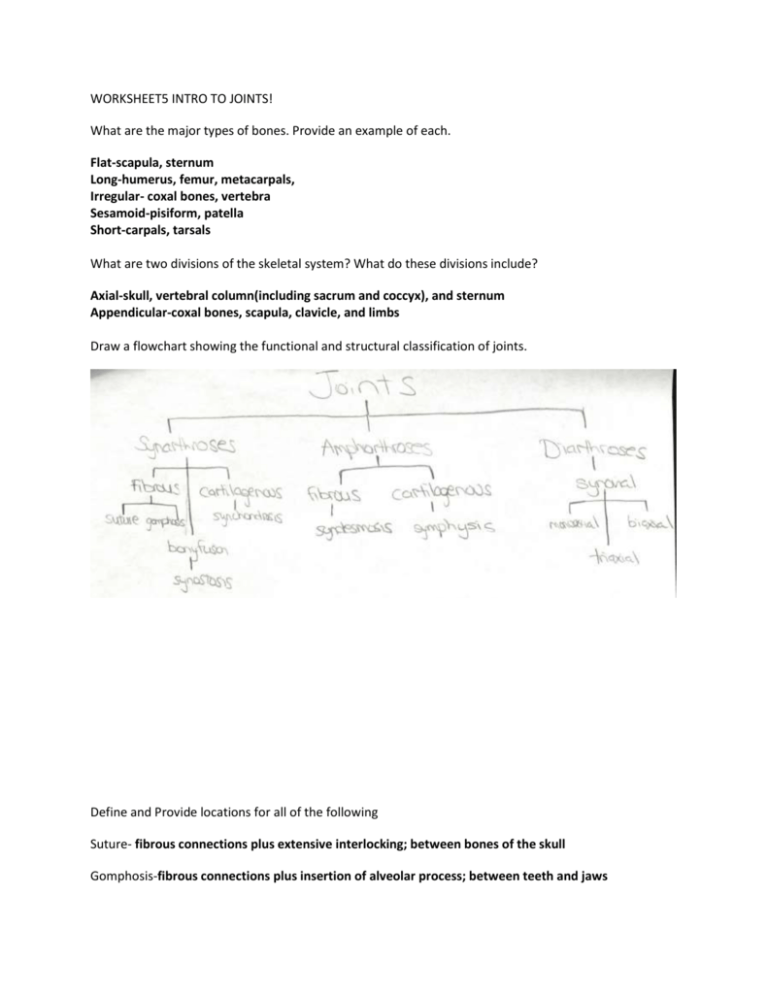
WORKSHEET5 INTRO TO JOINTS! What are the major types of bones. Provide an example of each. Flat-scapula, sternum Long-humerus, femur, metacarpals, Irregular- coxal bones, vertebra Sesamoid-pisiform, patella Short-carpals, tarsals What are two divisions of the skeletal system? What do these divisions include? Axial-skull, vertebral column(including sacrum and coccyx), and sternum Appendicular-coxal bones, scapula, clavicle, and limbs Draw a flowchart showing the functional and structural classification of joints. Define and Provide locations for all of the following Suture- fibrous connections plus extensive interlocking; between bones of the skull Gomphosis-fibrous connections plus insertion of alveolar process; between teeth and jaws Synchondrosis-interposition of cartilage plate- epiphyseal cartilages Synostosis-conversion of other articular form to a solid mass of bone-along frontal suture, epiphyseal lines Syndesmosis-ligamentous connection; between tibia and fibula, between radius and ulna Symphysis-connection by a pad of fibrous cartilage; between pubic bones, adjacent vertebral bodies Monoaxial joint-permits movement in one plane-elbow, ankle Biaxial joint-permits movement in two planes-ribs wrist Triaxial joint-permits movement in all three planes; shoulder, hip Name all characteristics that synovial joints share 1.joint capsule 2.articular cartilages 3. joint cavity filled with synovial fluid 4.synovial membrane lining the synovial cavity 5.accessory structures 6. sensory nerves and blood supply What are 3 functions of synovial fluid? 1.provides lubrication to reduce friction 2.nourishes chondrocytes (in cartilage), circulation is driven by joint movement 3.acts as a shock absorber when bones are subject to compression What are some accessory structures of joints? 1.Cartilage and fat pads 2.Ligaments 3.Tendons 4.Bursae-small fluid-filled pockets in connective tissue. Reduce friction and act as shock absorbers(where tendon or ligaments rub against other tissues What are the four types of angular motion (refers to changing the angle of the shaft)? Flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction What are some special terms given to specific articulations or unusual types of movement? Eversion, dorsiflexion, plantar flexion, lateral flexion, protraction, retraction, opposition, elevation, depression Provide the correct action term for the following descriptions Bending of the elbow-flexion Moving the humerus away from the midline- abduction Elevating the distal aspect of the foot-dorsiflexion Pad to pad contact of thumb with palm of fingers-opposition Twisting motion of the foot that turns the sole outward-Eversion Moving a part of the body anteriorly in the horizontal plane-protraction Describe the 6 subtypes of synovial joints and their location Plane Joints o AKA planar or gliding joints o Have flattened or curved faces o Movement is very slight o Found at the end of clavicles, between carpal bones, between tarsal bones, and between articular facets of adjacent vertebrae o May be nonaxial or multiaxial Hinge joints o Permit angular movement in a single plane o Monaxial joint o Elbow and knee Pivot joint o Monaxial like hinge joints o Permit only rotation o Joint between atlas and axis Condylar joints o AKA ellipsoidal joint o Oval articular face nestles within a depression on opposite surface o Biaxial joint, movement occurs across length of the oval o Between fingers and metacarpals and toes and metatarsals Saddle joints o Each articular face resembles a saddle (concave on one face, convex on the other) o Extremely mobile, extensive angular motion WITHOUT rotation o Biaxial o Thumb joint Ball-and-socket o Round head of one bone rests within a cup-shaped depression in another o ALL COMBINATIONS OF MOVEMENTS INCLUDING ROTATION CAN BE PERFORMED o Triaxial joints o Hip and shoulder