Skeletal System
advertisement

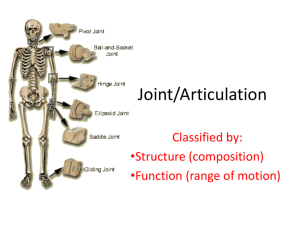
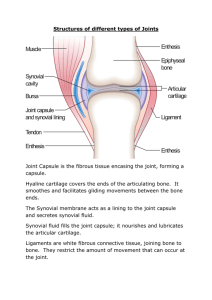
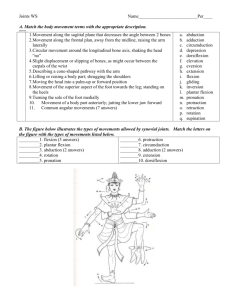
Skeletal System A. Functions: 1. Support for organs and other tissues 2. Movement-muscles need anchor to pull on to produce movement 3. Protection-of soft internal organs 4. Fat storage-yellow marrow in bones 5. Hematopoiesis-formation of red blood cells which carry oxygen. Making red blood cells. B. Components of Skeleton 1. Bones a. Long Bones-femur, humerus, tibia b. Short Bones-carpals, tarsals c. Flat Bones-ribs, skull, os coxa, scapula d. Irregular Bones-vertebrae 2. Bone marrow a. Red marrow-making red blood cells (hematopoeisis) b. Yellow marrow-stores adipose (energy) 3. Bone Joints (articulation) a. Fibrous Joints- fixed joints held together by dense CT---no appreciable movement (sutures of the skull bones) b. Cartilaginous Joints- hyaline or fibrous CT connects the bones forming the joint (joints between the vertebrae, symphysis pubis) c. Synovial Joints 1. Characteristics-Fully moveable joints, hyaline cartilage on articulating surfaces. Dense CT capsule surrounding the joint, inner layer of capsule has a layer of synovial membrane, which secretes synovial fluid. 2. Ball and socket joint- movement in many different planes. (shoulder and hip) 3. Hinge joint- Allows flexion and extension muscle actions at a joint (knee and elbow, phalanges) 4. Gliding or Plane Joint-Bones of the wrists and ankles (carpals and tarsals) 5. Saddle Joint-Thumb joint, movement in two planes, opposable thumb. 6. Pivot Joint-Rotation around a central axis 7. Condyloid or Ellipsoidal=Rotation around an axis, joint between the atlas and axis vertebrae of the neck (1st and 2nd cervical vertebrae)